人们经常想知道定性和定量 风险评估之间有何不同。在数字化的今天,有许多不同的 RBI(基于风险的检查)软件包可供选择,这是一个很好的问题。
让我们回过头来,先看看现有的风险评估标准。
有哪些标准?
There are several International engineering standards and recommended practices that outline requirements, methodologies, and the implementation of RBI. Examples are ASME PCC-3, RIMAP, DNV-RP G101, API 580, API 581, API 571, etc.
不同的标准通常适用于特定的行业领域。例如,ASME 是专门针对固定含压设备制定的美国标准;API 也是专门针对石油和天然气行业制定的美国标准;而 RIMAP 则是更适用于发电厂的欧洲标准。
人们有时会混淆不同类型的推荐实践。例如,API 580 概述了要求(如 RBI 评估中应包含的概念方法和必要元素),而 API 581 则概述了与 API 580 一致的方法。因此,RBI 软件包可以与概述要求(如 API 580)的最佳实践保持一致,而无需实施相关方法(如 API 581)。
标准有何建议?
标准通常不会只推荐一种方法(如只推荐定量方法)。例如,API 580 为使用 1 级(定性)或 2 级(半定量)或3 级(定量)方法实施 RBI 提供了指导(API 581 属于 3 级 RBI 方法)。(API 581 属于第 3 级 RBI 方法)。
不过,通常建议的是,RBI 方法和 RBI 小组研究方法必须是可辩护的、用户友好的、详细的、有记录的、透明的和可审计的。例如,为了与 API 580 保持一致,软件应实施一种用户友好型 RBI 方法,使负责的工厂检验工程师和运营工程师能够完全理解。否则,可能会导致设备风险增加,而不是降低风险。
标准还强调 RBI 技术方法(无论是 1 级、2 级还是 3 级)必须稳健。所选方法必须可靠地评估故障概率和适用的每种 DMs/FM(退化方法/故障模式)的风险概况,否则就无法确信最佳检查间隔。此外,团队研究方法必须确保识别所有 FM、运行限制、维护活动和其他风险缓解措施。
什么是定性、半定量和定量风险评估?
那么,现在我们知道,根据标准,定性、半定量和定量风险评估软件都是可以接受的,但区别在哪里呢?
我们先来看看定义。定量数据旨在收集冷冰冰的事实。数字。定量数据是结构化的、统计性的。定性数据收集的信息旨在描述一个主题,而不是衡量它。例如印象、观点和看法。半定量数据两者兼而有之。数据的某些部分是定性的,另一些部分是定量的。
因此,定量风险评估方法是根据确定风险的参数对风险进行定量估算。与此相反,在定性评估中,概率和后果不是用数字估算的,而是用高可能性、低可能性等限定词进行口头评估。
如果我们现在假定可以随时获得可靠的数据,那么全面的定量风险估算应该可以得出最精 确、最准确的结果。但是,我们必须注意以下几点。进行良好的定量评估所需的数据类型很难获得,而且需要花费大量时间,这往往会导致数据质量较低,也就意味着结果不够准确。
准确性是分析方法、数据质量和执行一致性的函数。精确度是所选指标和计算方法的函数。因此,在进行风险评估时,我们需要小心谨慎,因为评估结果可能非常精确,但如果概率和后果中仍然存在很多固有的不确定性,那么评估结果仍然是不准确的。
定性和定量 RBI 软件有哪些优点和局限性?
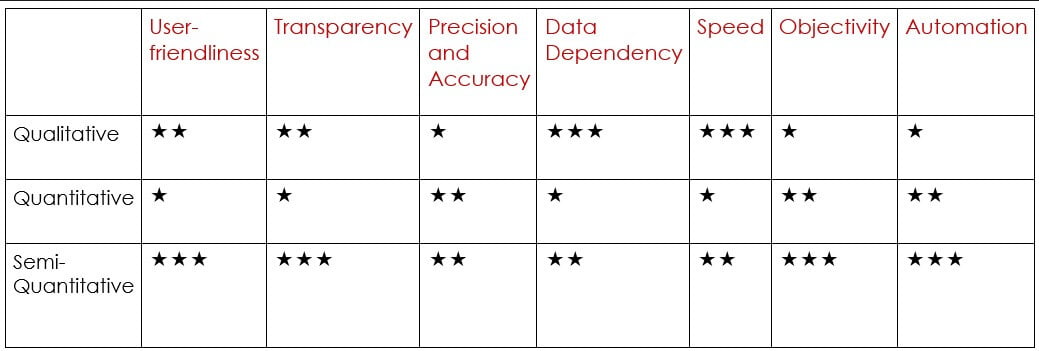
那么,哪种方法更好呢?没有简单的答案,因为定性、半定量和定量风险评估都可以取得成功。让我们先来比较一下典型的定性和定量风险评估:
- 用户友好性:这可能是定性分析的最大优点。由于定性分析不那么复杂,因此通常更容易让用户接受。
- 透明度:出于同样的原因,定性方法通常更容易完全理解。由于定量计算的复杂性,定量方法往往被当作黑箱来实施。
- 精确度和准确性:如果能够获得良好的数据,定量方法应在这一项中胜出,因为它们涉及对与每个设备项目相关的 PoF(故障概率)和 CoF(故障后果)进行严格的定量评估。我们必须记住,准确性将取决于概率和后果中固有的不确定性。
- 数据依赖性:定性分析需要的数据较少。
- 速度:由于定性RBI 分析需要的数据较少,因此通常要快得多。为定量 RBI 分析收集所有数据可能既困难又耗时。
- 客观性:定性 RBI 分析的结果在很大程度上取决于团队及其进行分析的专业知识,因此主观性较强。定量分析则更为客观。不过,我们也不要以为定量分析方法万无一失,要取得好的结果,仍然需要有经验的 RBI 和检验人员。
- 自动化:由于量化方法需要的团队投入较少,因此更容易实现自动化。
两全其美?
It is obvious that neither the qualitative nor the quantitative methodology is perfect. To increase the benefits and reduce the limitations, one can also go for the option of combining these two methods.
因此,半定量风险评估!这种方法往往通俗易懂,便于使用,而且更加准确。当然,它必须得到经验丰富的多学科团队研究的支持,以确保对结果的信心。然后,在风险评估的某些部分进行定性分析,在其他部分(根据置信度/敏感性分析选定)进行定量风险评估。
另一种两全其美的方法是,首先进行(更快的)高水平定性 RBI 分析,选出工厂中的高风险设施。然后只对这些高风险设施进行定量 RBI 分析。请记住,要获得准确的结果,良好的数据和经验丰富的多学科团队研究仍是必要条件。
Explore the Right RBI Approach for Your Operations
At Cenosco, we understand that every asset strategy is unique – which is why we support a range of Risk-Based Inspection (RBI) methodologies, from qualitative to fully quantitative, aligned with API 580 and API 581 guidelines.
Our IMS (PEI) software has long supported the S-RBI methodology, a Shell-developed Risk-Based Approach, compliant to API 580 and to API 571’s damage mechanisms. This can be implemented as either qualitative or semi-quantitative. For the semi-quantitative methodologies, it uses specific calculators (e.g. liquid release, CUI, SSC, and other corrosion prediction models) and detailed questionnaires, to calculate StF (Susceptibility to Failure) and CoF (Consequence of Failure), based on the most relevant failure modes. When using the S-RBI methodology IMS PEI allows users to swap between methodologies for each RBI Analysis. The default is the semi-quantitative methodology since this is preferred by most customers.
Since 2025 we also provide comprehensive support for a fully quantitative API 581-based RBI methodology, specifically for pressure equipment such as piping, vessels, and tanks. Our flexible and standards-aligned approach ensures you can apply RBI effectively across a wide range of assets. Our implementation follows the 2016 edition of API 581, including the 2019 and 2020 addenda – offering a stable and trusted foundation. It includes features like configurable failure frequencies and interval target configurations.
Whether you’re just starting with RBI or refining an existing program, we can help you choose the approach that best suits your operations – be it qualitative, semi-quantitative, or fully quantitative in line with API 580/581.
Also, remember IMS PEI is not a standalone RBI tool. It integrates the RBI results with inspection results, wall thickness measurements/calculations, and schedules. The RBI results can thus be used to define the next inspection dates that feed into the IDMS part of the tool, which can, in turn, interface with the site’s CMMS (Computerized Maintenance Management Software) (e.g. SAP).
准备好演示了吗?
您准备好观看 IMS 套件的实际操作了吗?请填写下表预约演示!

Elsa Tolsma-de Klerk Technical Writer
Elsa is an engineer with a passion for sharing knowledge. She holds a Master’s in Electronic Engineering and spent over a decade at Sasol as an Advanced Process Control Engineer, where she gained hands-on experience in optimization, control systems, and writing technical documentation. Since 2019, she’s been a Technical Writer at Cenosco, now leading the IMS knowledge base and training Academy team.




