Ensuring the integrity of heat exchanger tubes is critical and challenging when it comes to maintaining industrial efficiency. Heat exchangers are vital components in various industries, playing a key role in transferring heat between fluids.
However, inspection becomes a BIG and DIRTY job with bundles containing anywhere from 250 to an overwhelming 5000 tubes. Traditionally, due to concerns over tube conditions and the potential for corrosion in heat exchangers, sites often inspect every single tube. This process is not only laborious but also incredibly time-consuming.
Imagine spending 12 hours just cleaning and inspecting a mere 300 tubes! Moreover, certain corrosion inspection techniques like the Internal Rotary Inspection System (IRIS) necessitate substrate materials to be cleaned meticulously for effective results. Often, this means multiple rounds of washing and inspecting to get accurate data.
Enter Extreme Value Analysis (EVA) – a statistical method revolutionizing how we approach this daunting task. By employing EVA for efficient heat exchanger tube wall thickness calculations, we can confidently reduce the number of tubes inspected without compromising safety or performance.
This not only slashes inspection times significantly but also translates into substantial cost savings. Additionally, EVA helps extend the heat exchanger’s useful life by accurately assessing tube conditions. In this blog, we’ll explore how EVA transforms the heat exchanger inspection process, making it smarter, faster, and more efficient.
应用极值分析 (EVA) 计算热交换器壁厚
极值分析 (EVA) 是一种强大的统计方法,用于预测数据集中的最极端值。在热交换器方面,EVA 特别适用于计算较小的、有代表性的管子样本的最大壁厚损失。该过程从取样开始,从热交换器内具有代表性的管子中读取壁厚读数。
收集数据后,将其拟合为统计分布,通常是 Gumbel 分布。这一拟合过程有助于了解数据集中极端值的行为。利用该分布,可以推断出整个热交换器的最大壁损,从而全面了解潜在的降解情况。
在此基础上,必须计算出热交换器管壁厚度随时间的变化情况。通过了解壁厚的变化情况,就可以预测热交换器的剩余使用寿命。这些信息对于规划检查和确保设备的最佳性能至关重要。
换热器管壁厚度计算步骤
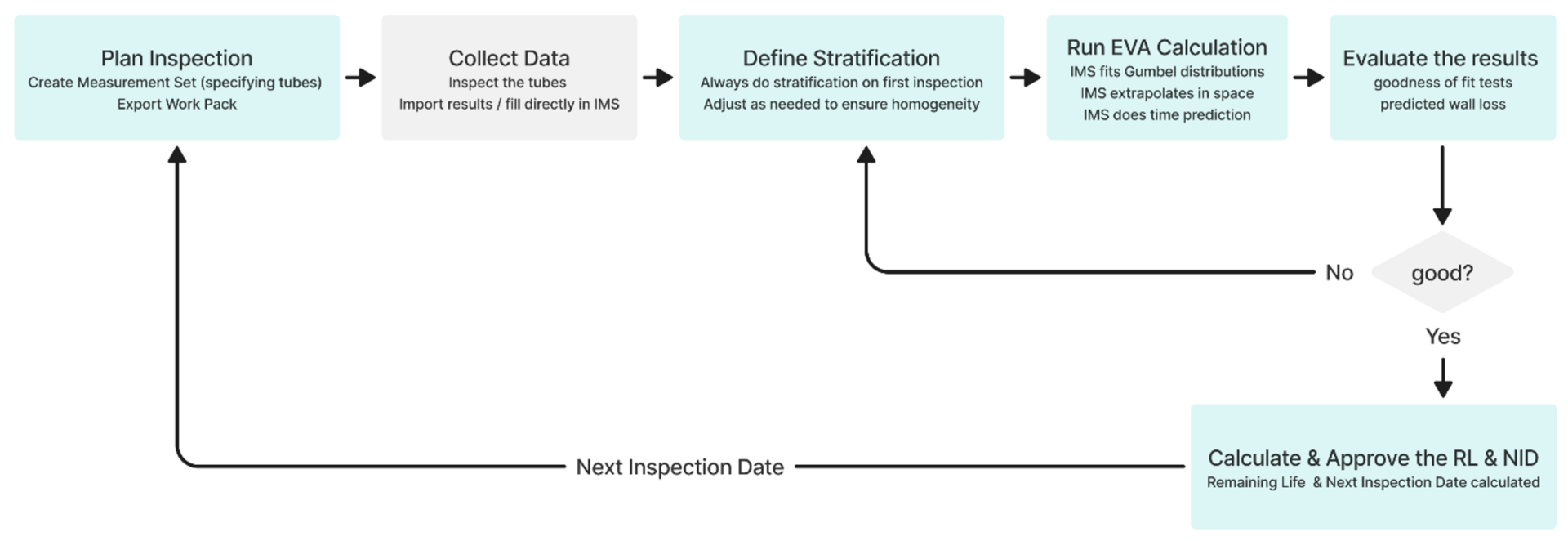
既然我们已经了解如何将 EVA 应用于换热器管壁厚度计算,那么让我们来探讨一下如何实际实施这一过程。我们将以IMS PEI软件的工作流程为例进行说明。以下是该流程的逐步分解:
- 计划检查:首先指定需要测量的管道。准备并输出检查所需的文件。
- 收集数据:对选定的试管样本进行检查。这可能涉及 IRIS 等技术,这些技术要求对基底材料进行高标准的清洁,以获得有效的结果。
- 定义分层:分层通过创建更小的、一致的组群(称为分层)来帮助管理不一致的数据。根据需要调整分层,可确保各层数据的一致性,这对准确分析至关重要。
- 运行 EVA 计算:计算使用 Gumbel 分布来模拟所收集数据中的极端值。这样就可以推断出整个热交换器的最大管壁损耗。传统的腐蚀速率模型用于估算管壁厚度随时间的变化。(在这种情况下,EVA 计算使用 IMS PEI 软件进行)。
- 评估结果:进行拟合优度测试,评估拟合分布的质量。如果结果不能令人满意,则返回分层步骤,以确保样品均匀。此外,还要评估预测的壁面损失,确保充分了解热交换器中的腐蚀行为。
- 计算并批准剩余使用寿命和下次检查日期:根据 EVA 结果,计算热交换器的剩余使用寿命并确定下一次检查日期。这又回到了计划下一次检查的初始步骤。
下一张图片直观地展示了这一工作流程,提供了整个流程的清晰概览。
确保准确计算管壁厚度:热交换器检查的最佳实践
在收集钢管壁厚数据时,必须确保样本的质量和代表性。我们强烈推荐使用内部旋转检测系统 (IRIS) 等进行高质量检测,因为它们能提供准确可靠的数据。不过,即使是低质量检测,其结果也往往比较保守,仍然可以使用。
样本应代表整个热交换器,且均匀一致,以准确反映设备状况。下图显示了典型的代表性样本(左)与缺乏足够分散性的非代表性样本(右)的对比。
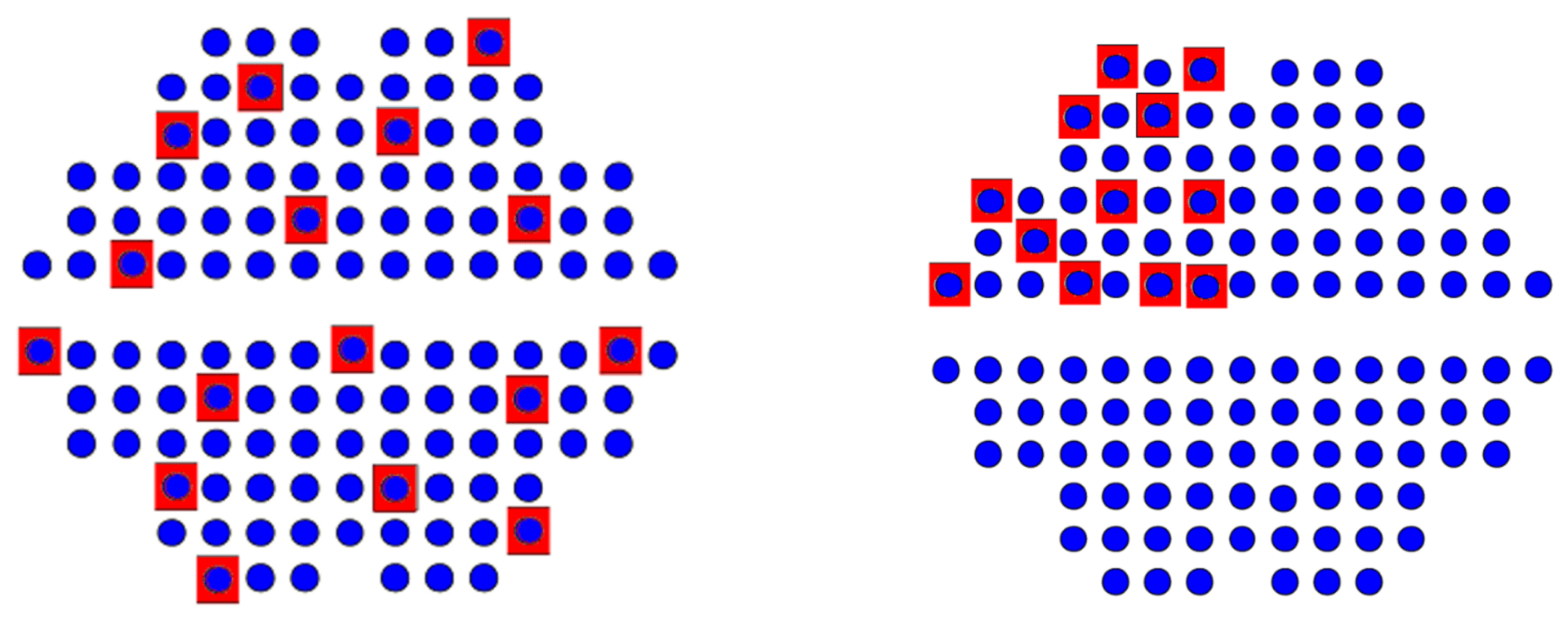
Homogeneous data shows no significant variations or localized areas with higher or lower corrosion rates. When the data is non-homogeneous, stratification is needed. This involves dividing the data into smaller, more uniform groups or strata.
For example, the inlet and outlet sides of the heat exchanger might be separate strata since temperature differences affect corrosion rates. It’s recommended to sample 20-25% of the tubes per stratum, as sampling more could result in overly optimistic estimates. For the first inspection, when establishing a baseline, inspecting up to 100% may be necessary. By following these guidelines, you’ll ensure that your tube wall thickness readings are accurate and reliable.
评估统计模型的拟合度:统计方法与图形方法的结合
在将 Gumbel 等分布拟合到数据后,必须使用统计和图形方法评估拟合的好坏。统计方法包括假设检验,如评估整体拟合质量的 Kolmogorov-Smirnov 检验和强调分布尾部的 Anderson-Darling 检验。这些检验为衡量 Gumbel 分布对数据的代表程度提供了量化指标。
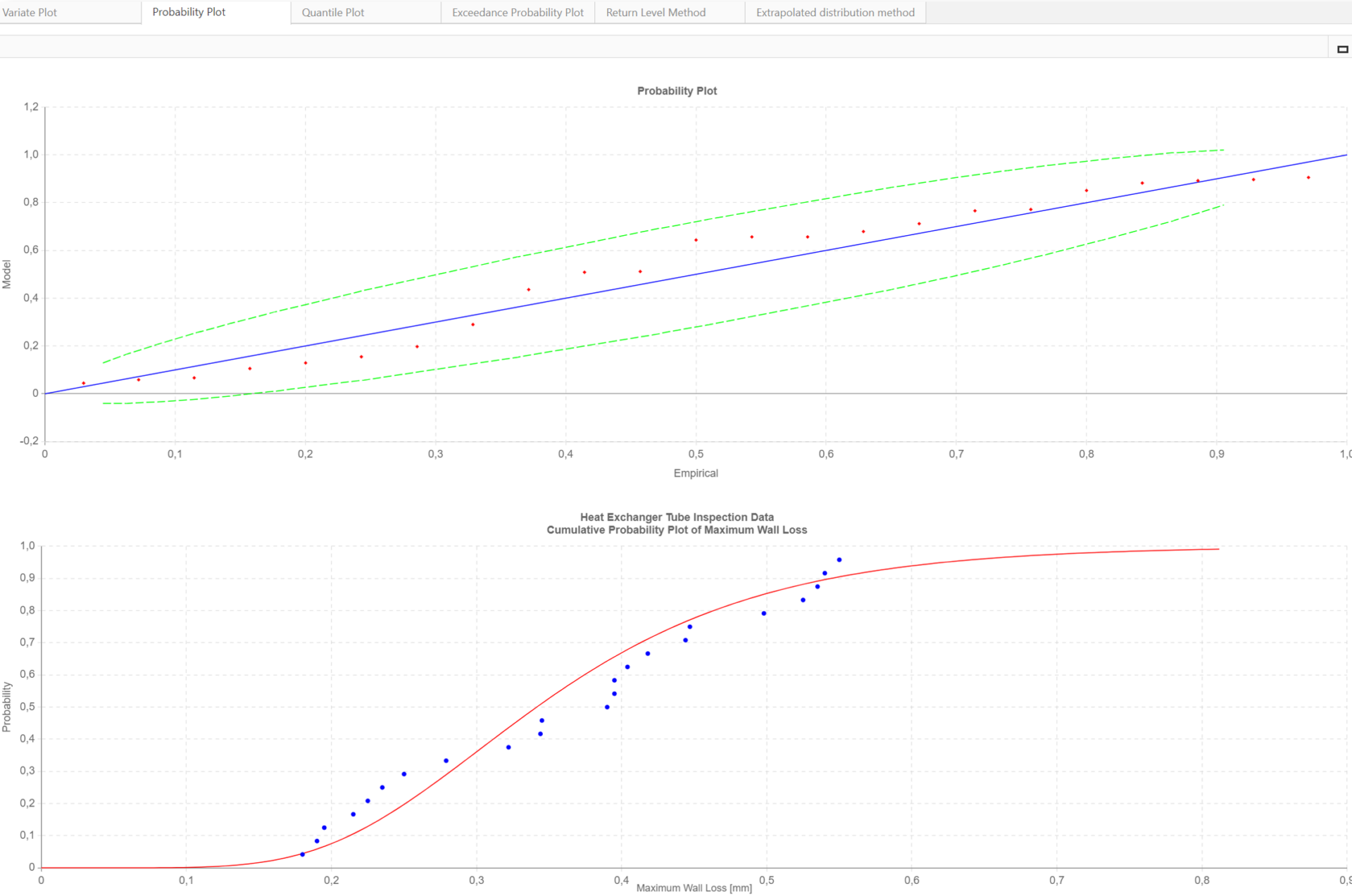
In addition to statistical methods, graphical methods should be used to better understand the fit. These include probability plots, exceedance probability plots, and quantile plots.
For example, the quantile plot shown below compares theoretical quantiles to sample quantiles. A quantile divides a dataset into equal-sized intervals (e.g., the median is the 50th quantile, meaning half the data points are below it). If the fit is good, the points in the quantile plot will align along a straight line. The plot includes a line of perfect fit (blue) and confidence bands (green) to highlight deviations.
If most points (red) lie close to the line and within the bands, it indicates the theoretical distribution fits well.
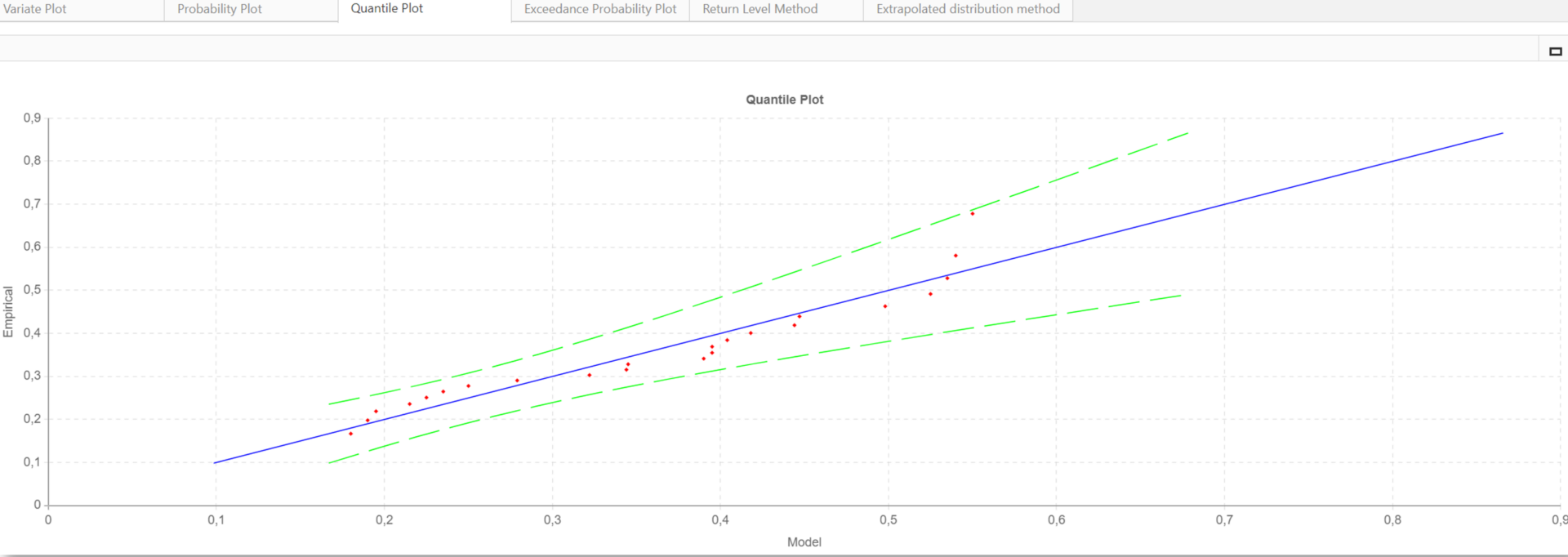
这些可视化工具有助于识别仅通过统计测试可能无法发现的差异或模式。关键是不能只依赖统计方法。在得出结论之前对图形方法进行审查,可确保进行更可靠的拟合评估。此外,还应始终对预测的壁厚损失进行评估,确保对腐蚀行为有充分的了解。
计算整个热交换器的管壁厚度
目的是统计推断整个热交换器的最大壁损。有两种方法可用于此目的:回归水平法和外推法。这些方法有助于确定最可能的最大壁损(极值)及其置信区间(CB)。现在我们来看一个直观的示意图,帮助我们理解壁厚损失值的分布和相关的置信区间。
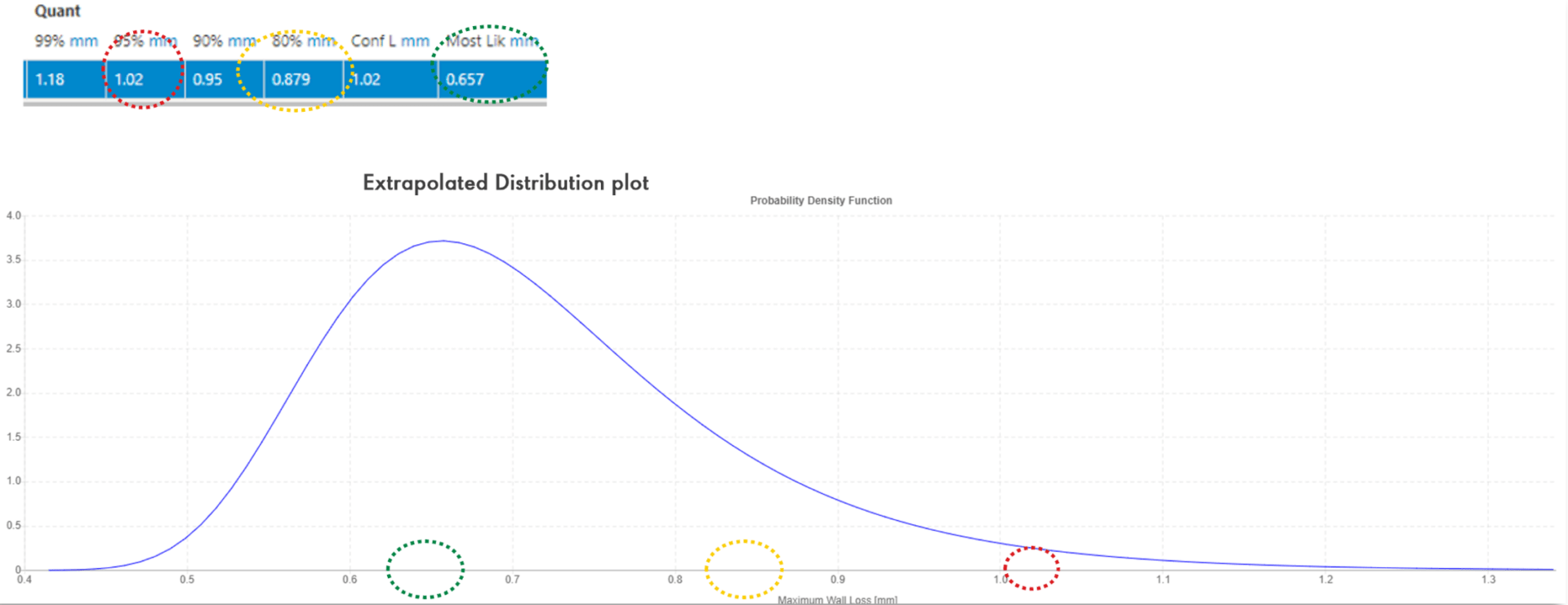
The image above shows an Extrapolated Distribution plot featuring a probability density function curve. The curve peaks at the most likely maximum wall loss value (highlighted by the green circle). It tapers off at both ends, illustrating the distribution of potential maximum wall loss values.
Quantile values, such as the 95th quantile at 1.02mm (marked by the red circle), indicate confidence bounds. This means 95% of the expected maximum wall losses are below 1.02mm, while 80% of the expected maximum wall losses are below 0.879mm (indicated by the yellow circle)
案例研究:带有三个热交换器的原油预热器的极值分析
我们的案例研究侧重于检查一个有三列运行中的粗预热器。这些热交换器已经运行了 25 年,达到了设计寿命,客户希望将其寿命至少再延长十年。以前,每隔一段时间就会进行目视内径检查,以评估管道状况,但这些检查只能提供定性数据,而无法测量壁厚。客户需要确定是否有必要进行更换。
在使用寿命结束前一年的计划停机期间,使用具有代表性的样本对热交换器进行了检查。这样就可以估算出最大的壁厚损失,并帮助决定继续运行十年是否安全。
All three heat exchangers had similar results, and we’ll concentrate on one of them. The heat exchanger bundle consists of 120 carbon steel tubes, 23 of which were inspected. Knowledge from previous borescope inspections helped identify the best tubes to examine. The renewal thickness was set at 1.1 mm, with a nominal wall thickness of 2.4 mm.
The inspection took place on October 1, 2023.
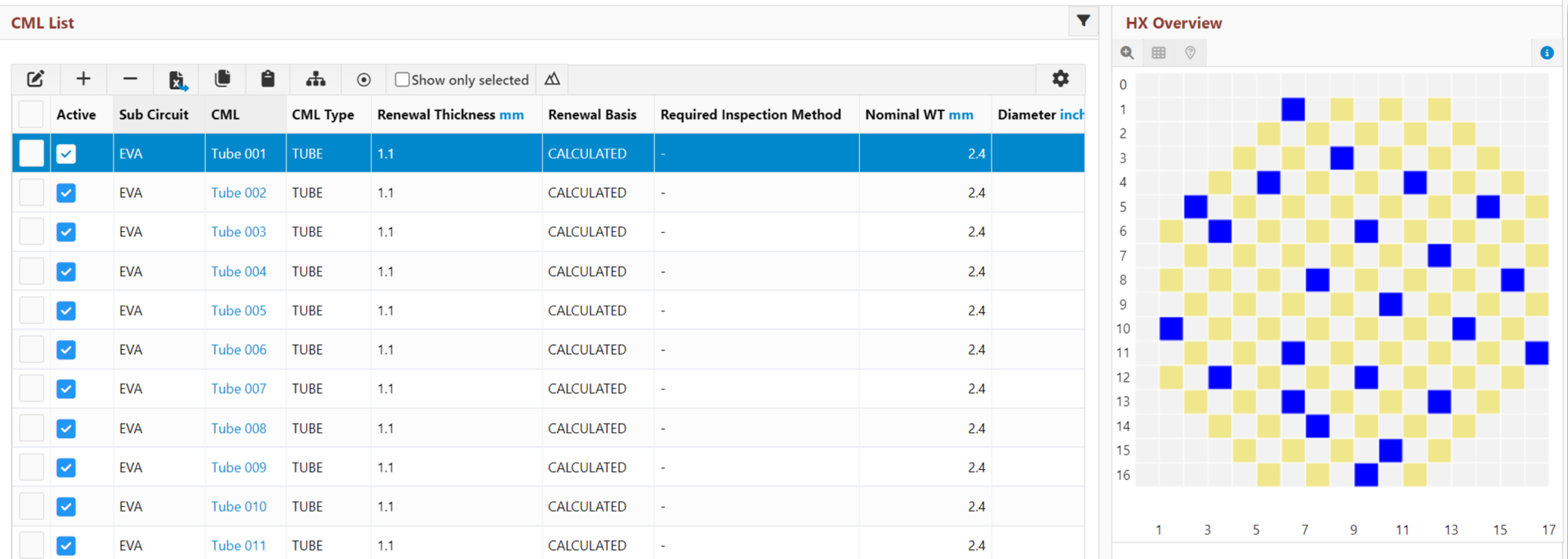
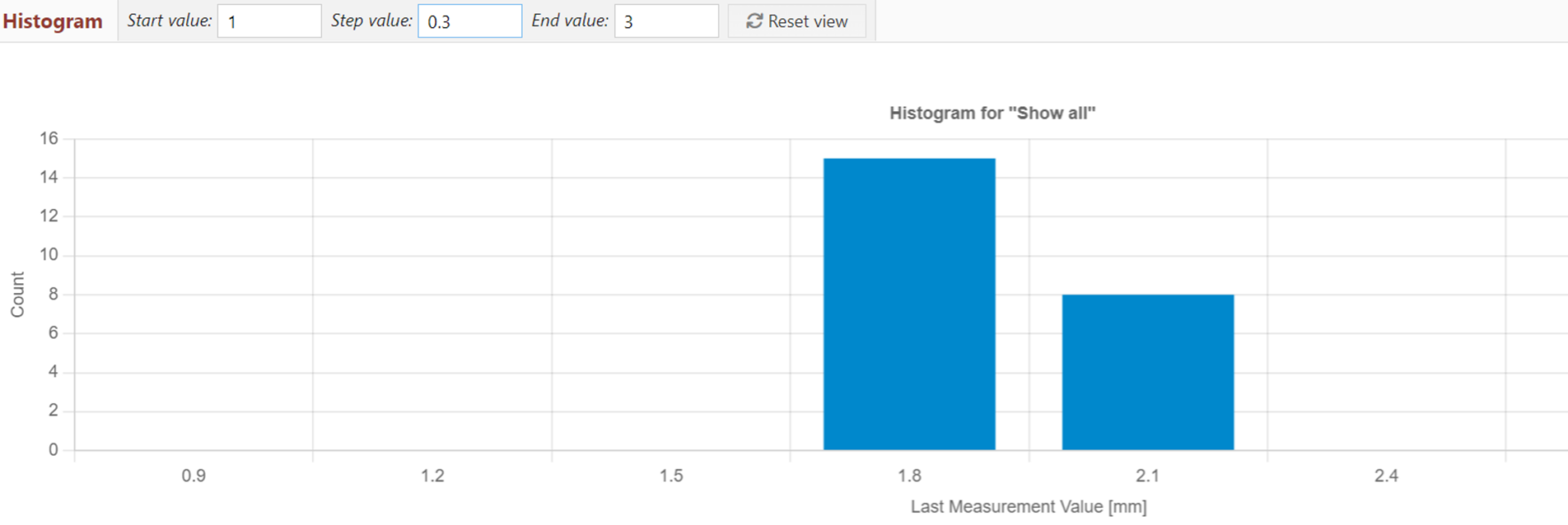
对于该热交换器来说,单一的均匀分层就足够了。如下面的直方图所示,没有明显的差异,也没有腐蚀率较高或较低的局部区域;腐蚀率值在一个很小的范围内。这证明所收集的数据代表了整个热交换器,为了解其状况提供了可靠的信息。
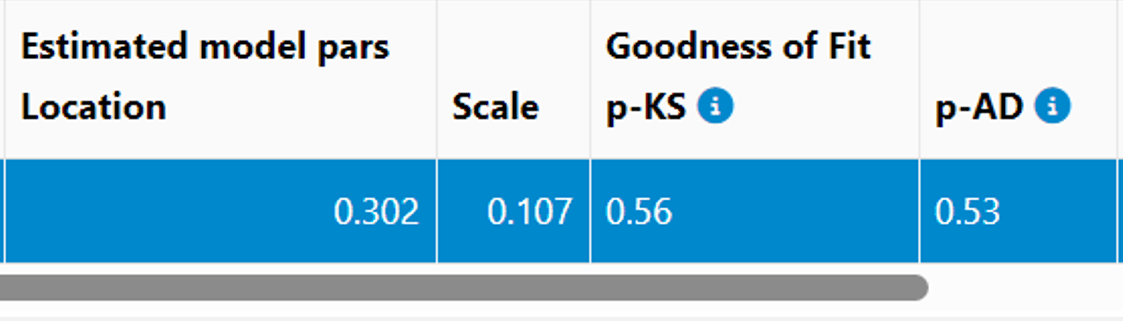
评估所获统计模型的拟合度
统计检验和图形方法表明数据拟合良好。Kolmogorov-Smirnov (p-KS) 和 Anderson-Darling (p-AD) 检验的 p 值均大于 0.5,证实了拟合的质量(见下文结果)。
图表还显示,理论分布与样本数据十分吻合,为分析提供了信心,并确认了良好的拟合度。您可以在下面的概率图中看到这一点。
Extrapolating the Tube Wall Thickness in Space
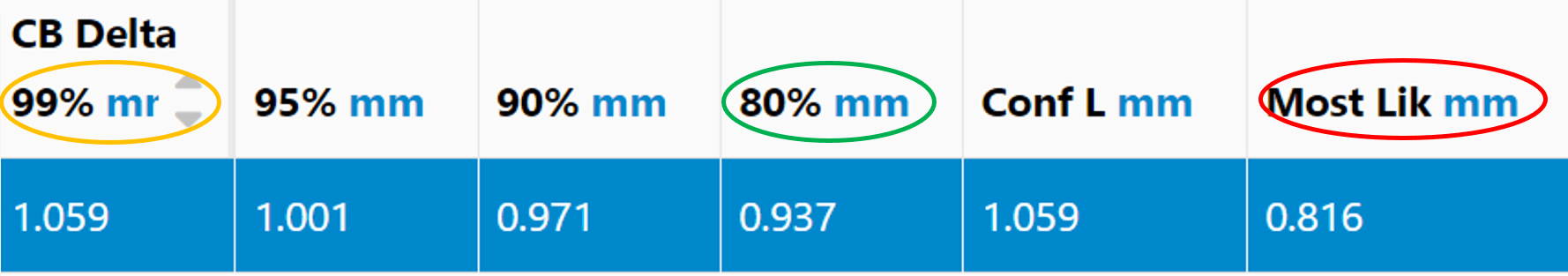
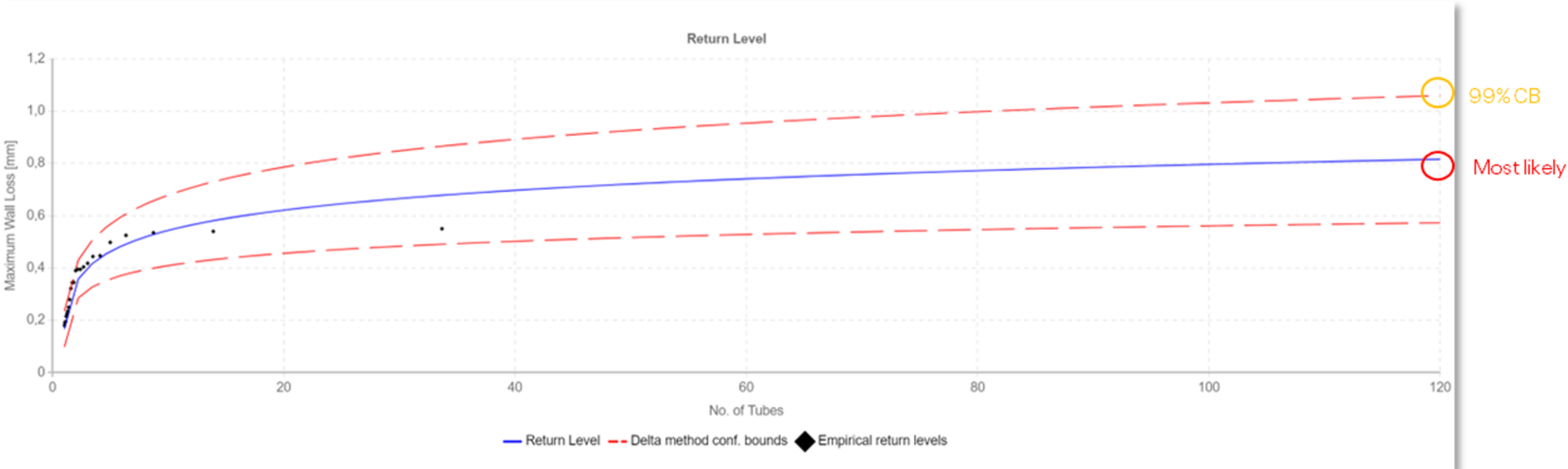
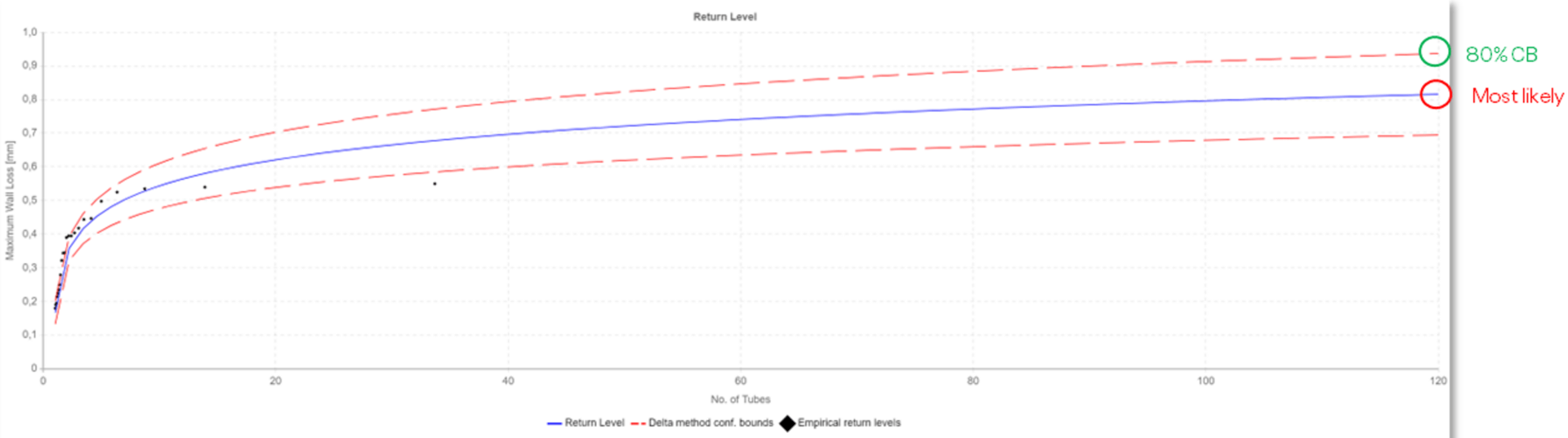
Next, the Return Level Method was used to extrapolate the data in space to calculate the maximum wall loss for the entire heat exchanger. The most likely maximum wall loss was 0.816 mm (indicated in red). At the 99% confidence bound, the maximum wall loss was 1.059 mm (indicated in yellow), and at the 80% confidence bound, it was 0.937 mm (indicated in green). The graphs below illustrate these findings.
The upper graph shows the return level curve with the 99% confidence bound, while the lower graph shows the curve with the 80% confidence bound. As you can see, higher confidence bounds lead to more conservative estimates, showing greater wall loss, indicating a thinner remaining tube wall thickness and a shorter useful life for heat exchangers.
计算热交换器的使用寿命和下次检查日期
根据不同的置信区间计算出了热交换器的最小剩余管壁厚度和腐蚀率。通过这些计算,可以确定热交换器的使用寿命、最大检查间隔和下次检查日期。
下面的图片展示了结果的详细分类。首先,两个表格显示了热交换器的最小剩余壁厚和不同置信度(95%、90% 和 80%)下的腐蚀率。
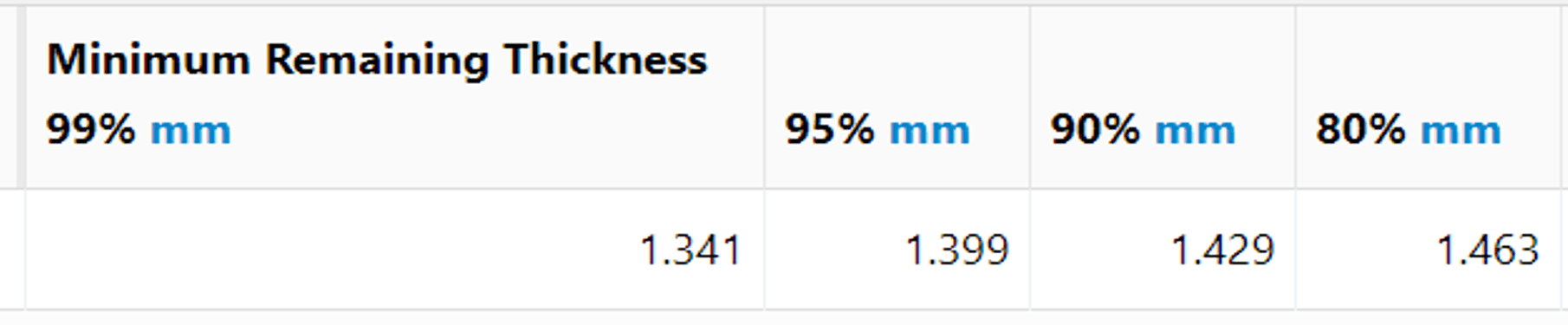
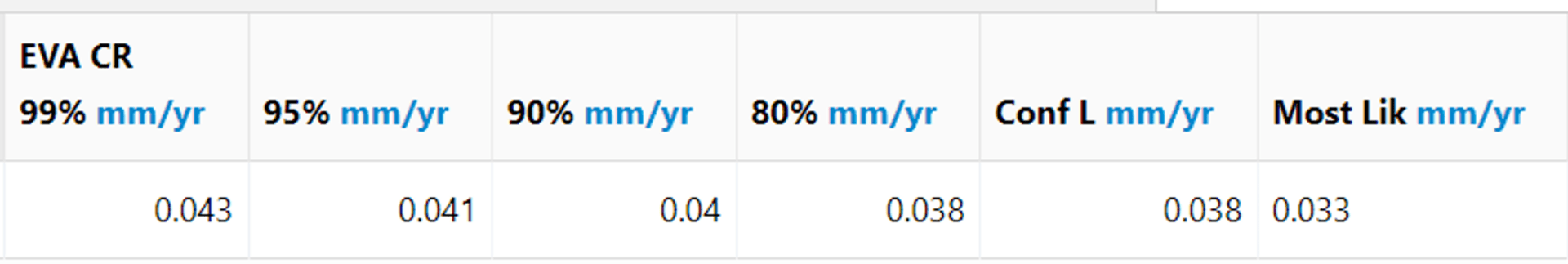
The calculation summary then shows the heat exchanger’s useful life (Remnant Life), corrosion rate (Rate), and next inspection date (Next Insp Date) at the 80% confidence level. It’s important to note that the corrosion engineer determines the choice of confidence bound. Typically, using a representative sample and conducting multiple inspections over time increases confidence in the results, allowing for the use of lower confidence bounds.
In this case study, the information gathered from previous borescope inspections gave the engineers enough confidence in the new results to select the 80% confidence bound.
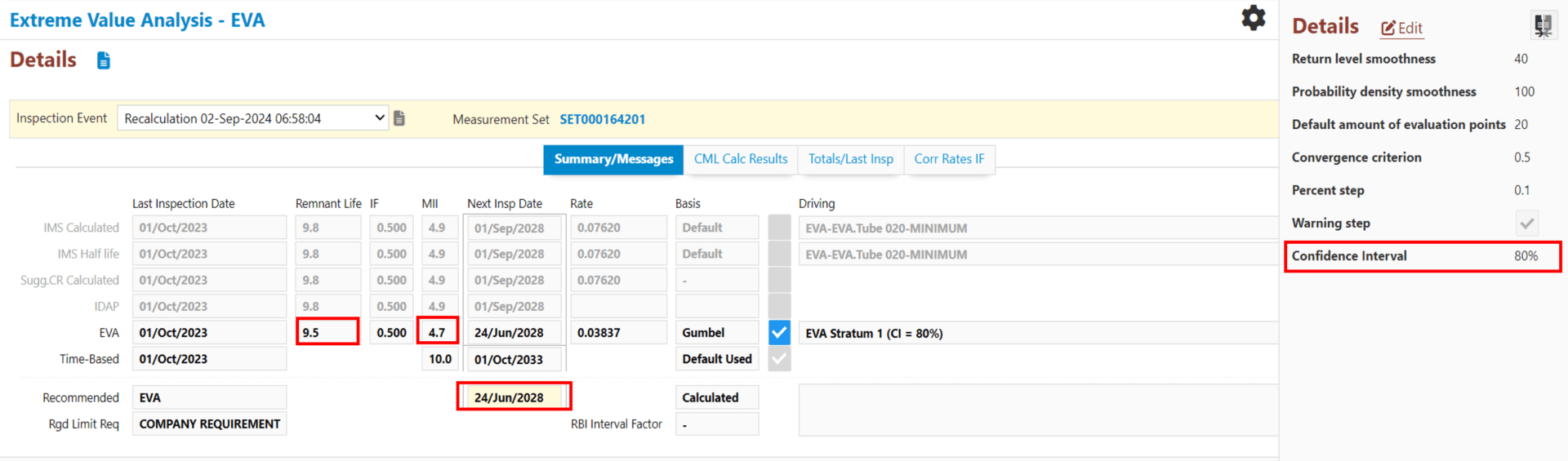
热交换器的使用寿命估计为 9.5 年(接近预期的 10 年延长期),根据行业标准的半衰期概念,最大检查间隔 (MII) 为 4.7 年,下次检查时间为 2028 年 6 月 24 日。以下是计算结果(置信度为 80%):
剩余寿命=(最小剩余厚度-更新厚度)/腐蚀率=(1.1463 毫米-1.1 毫米)/0.038 毫米/年=9.5 年
下次检查日期 = 上次检查日期 + 剩余寿命 ∗ IF = 2023 年 10 月 1 日 +9.5*0.5 = 2028 年 6 月 24 日
这些结果让工程师们对热交换器的状况充满信心。他们没有选择全面更换,而是放心地采取必要的措施,使热交换器能够再运行十年。如果估计的使用寿命更短,他们可能会考虑其他方案,比如使用腐蚀抑制剂来减缓热交换器中的腐蚀。不过,他们现在知道,在下次检查之前不需要采取任何行动。
案例研究结果:缩短检查时间和周转时间
The benefits of using this heat exchanger tube wall thickness calculation approach were significant. By conducting inspections on a representative sample, engineers reduced overall inspection time and preparation activities by at least 40%, streamlining the entire process.
Due to the heat exchangers being part of the critical path, the turnaround time was also shortened by 12%, allowing production to restart sooner than expected. Additionally, a deeper understanding of risks and threats led to an estimated 85% cost savings by avoiding expensive maintenance actions like repairs and replacements. These advantages highlight how EVA makes the heat exchanger inspection process smarter, faster, and more efficient.
结论EVA 可确保高效和自信的检查
In summary, EVA provides significant time and cost savings for inspections and tube cleaning while ensuring they are performed at the right intervals. By using a representative sample and conducting multiple inspections over time, the conservatism in models can be minimized.
This makes EVA a reliable framework for efficient heat exchanger inspections. For added assurance, IMS PEI allows for independent assessment of tube degradation risks, which can be combined with EVA to determine the optimal time for the next inspection.
请填写下表,了解 EVA 和 IMS PEI 的活动。
想进一步了解 IMS?
请在下方申请演示,以获得其功能的第一手资料!

Elsa Tolsma-de Klerk Technical Writer
Elsa is an engineer with a passion for sharing knowledge. She holds a Master’s in Electronic Engineering and spent over a decade at Sasol as an Advanced Process Control Engineer, where she gained hands-on experience in optimization, control systems, and writing technical documentation. Since 2019, she’s been a Technical Writer at Cenosco, now leading the IMS knowledge base and training Academy team.