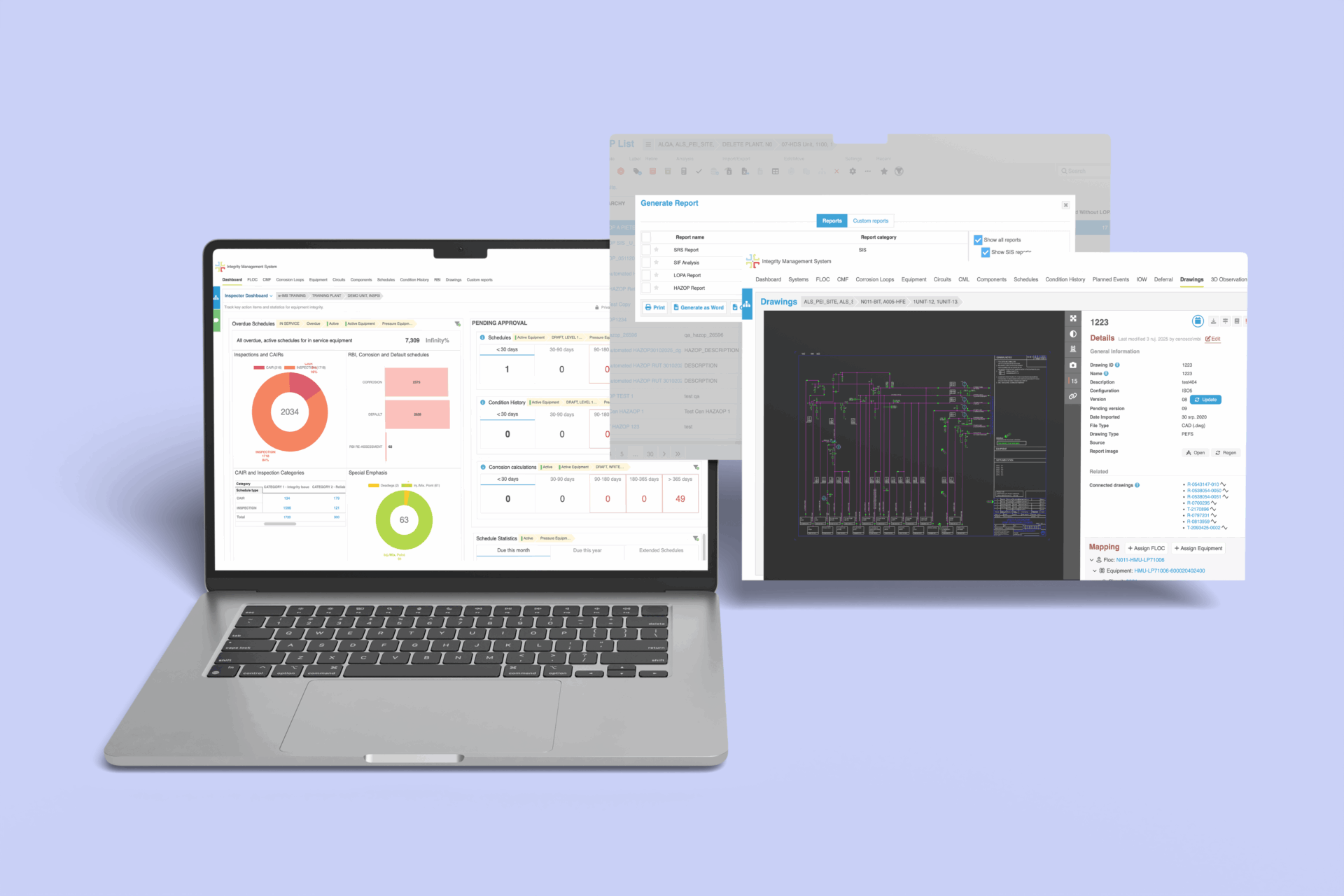
If you have been following us this year, you already know our core focus for IMS product development: simplifying complex workflows to boost productivity and enabling engineers to make informed, high-impact decisions. Our vision remains to scale up our IMS platform into a truly connected ecosystem, enabling asset data to flow seamlessly across IMS modules, other systems, and providing you with a comprehensive view of your assets. The intention is to allow you to focus on critical engineering tasks while delegating repetitive data entry to a reliable and intelligent platform.
In this blog, we’re excited to share some of the most significant enhancements from our recent releases in the latter half of 2025. These updates not only deliver on that promise but also build upon substantial improvements introduced earlier this year, which have already earned appreciation from users worldwide.
Grouped across different themes, we have a list of improvements that we have launched this year:
1. Productivity and usability: Workflow automation that speeds up your work
Efficiency in asset integrity workflows depends on minimizing unnecessary steps. Ideally, we want every query, filter, and upload you execute within our IMS to have minimal latency and predictable behavior. To achieve this, we have introduced capabilities that optimize data retrieval, reduce manual input, and standardize repetitive operations, ensuring our users spend less time navigating interfaces and more time applying engineering judgment.
- Min/Max filters (Applicable across all IMS modules)
Quickly filter the earliest inspection dates, most recent condition histories, or lowest remaining life values grouped by the property that is the most relevant to you. This filtering functionality eliminates the need for manual sorting or exporting to spreadsheets. For example, you can use it to find Circuits with the lowest Remnant Life per Unit, most recent Condition Histories per Equipment, or following due Schedules per Responsible Person, on the entire dataset.
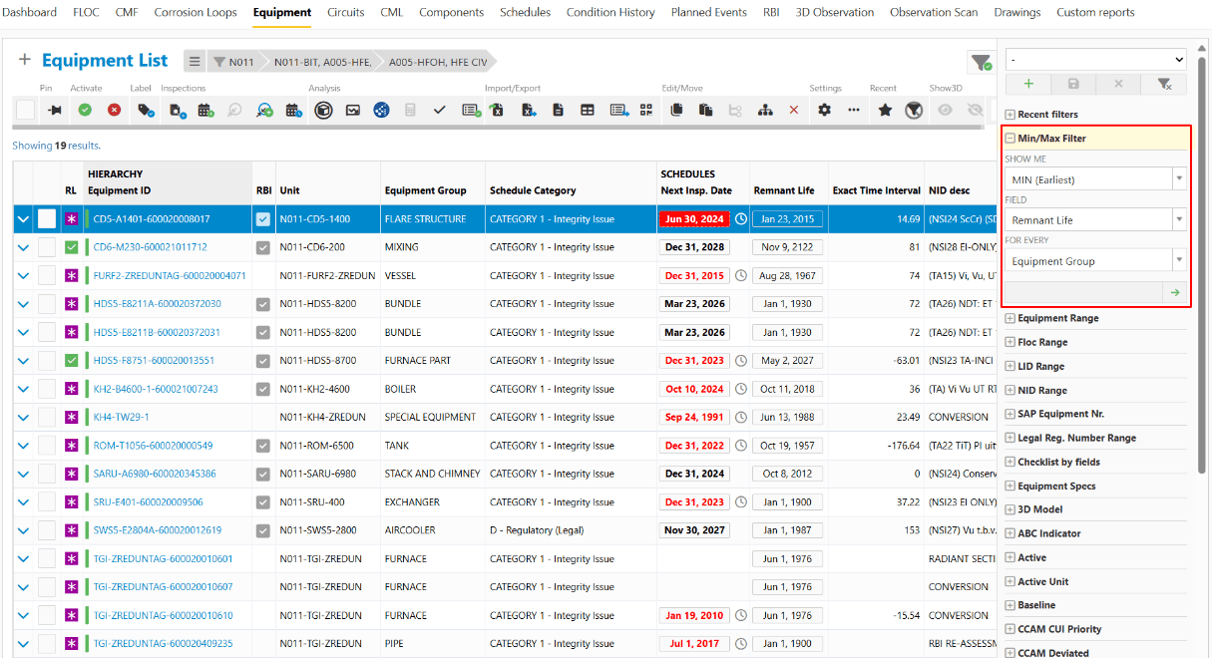
Filter based on the most numeric or date fields
For more information on the new Min/Max filters, refer to the IMS Handbook.
- IMS drawings & documents enhancements (Applicable across all IMS modules)
From interactive previews to directly linking equipment to the drawing uploaded, managing drawings is now faster and easier. The recent releases enable you to preview drawings without leaving the main IMS grid, upload and connect drawings to equipment in one step, assign custom names to avoid confusion with duplicate filenames, replace existing drawings with newer versions, and track changes with an enhanced event history and exportable logs. Additionally, automatic and manual CML mapping, along with improved hierarchy views, make CAD integration seamless.
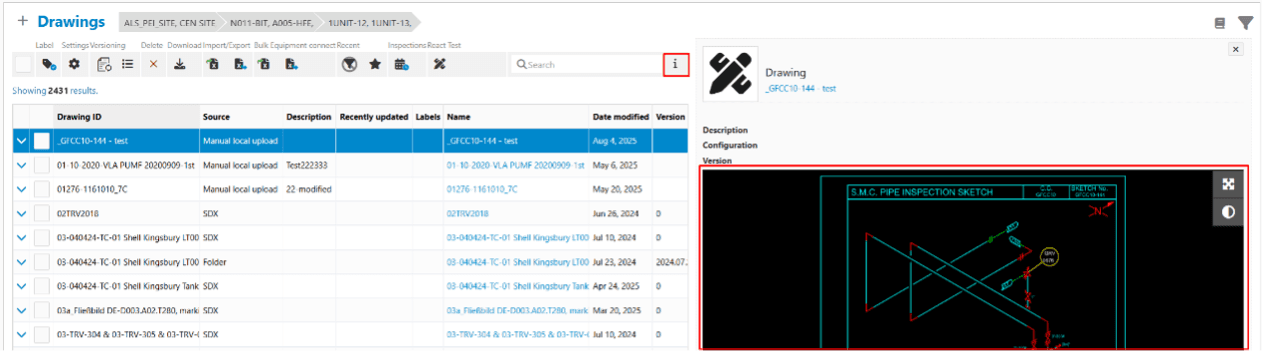
Preview your drawing attachment from the Main grid

Link the Equipment with the Drawing during upload
IMS Drawings and documents management has seen several improvements this year. For a comprehensive overview of all the new changes in Drawings and Documents management, check under the respective IMS Improvements in the Release Notes or the IMS Drawings section in the IMS Handbook.
- Inspection locations (Applicable for IMS PEI and IMS RCM)
Inspection point can now be defined across all modules, extending functionality beyond IMS PLSS to IMS PEI and IMS RCM. This makes it easier to track precisely where inspections occur, ensuring they are trackable, as well as easier for field personnel to identify and carry out their activities.
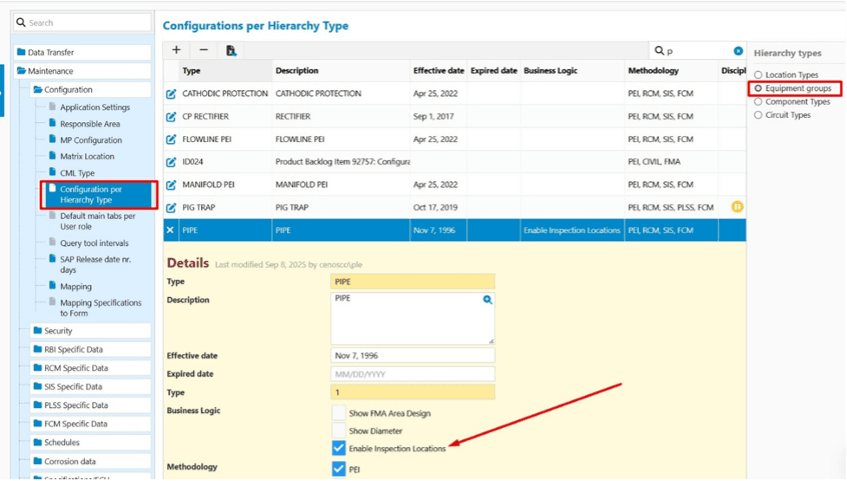
Option ‘Enable Inspection Locations’ under Settings to toggle this feature
For more information on the option to Enable Inspection Locations, refer to the Release Notes
2. Better decision-making and compliance take priority
Accurate decision-making in asset integrity workflows requires validated data and strict adherence to engineering standards. Our recent IMS releases incorporate compliance logic as per engineering standards and quantitative methodologies directly into IMS, enabling you to perform risk-based planning with confidence.
- Carry out RBI study as per API RBI 581 in IMS PEI
IMS PEI now supports API 581 Risk-Based Inspection methodology (2016 edition, including 2019 and 2020 addenda), in addition to the existing S-RBI approach, for pressure equipment, including piping, pressure vessels, and tanks. This capability provides you with the choice to select the most appropriate risk assessment method, qualitative, semi-quantitative, or fully quantitative, while maintaining compliance with API 580 principles. Furthermore, the IMS RBI calculations in our IMS PEI software have been independently validated and certified by SGS, ensuring conformity with API RP 581 requirements and assuring that all risk calculations are based on audited and verified algorithms.
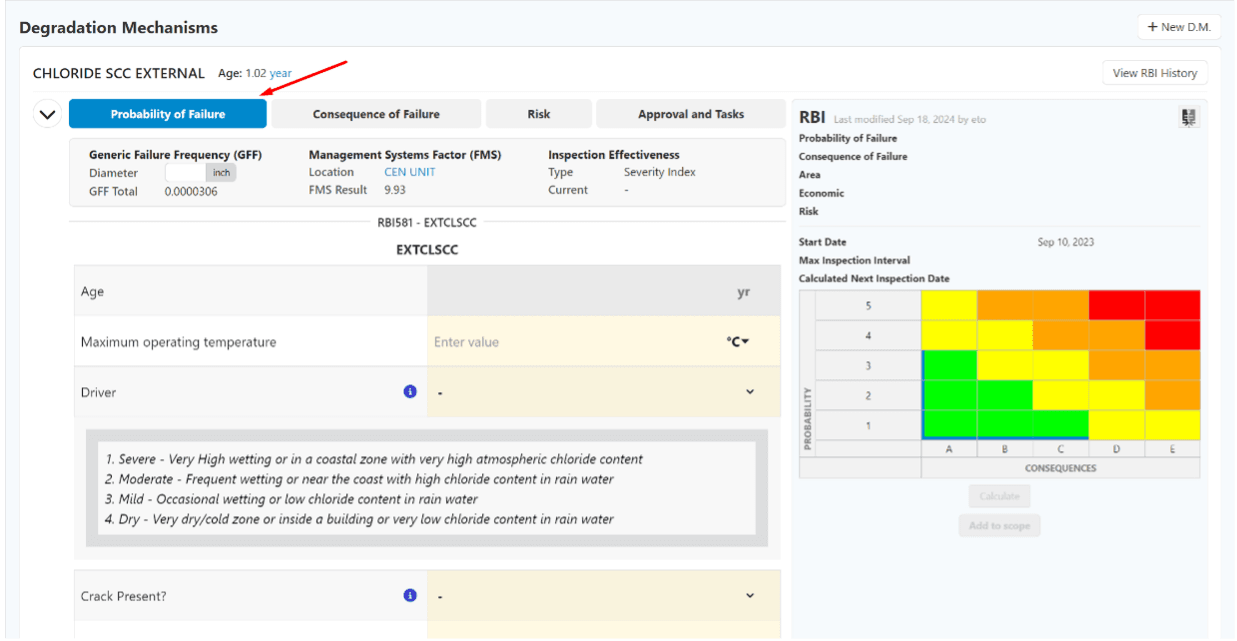
Probability of Failure (PoF) as per API 581
For more information on API RBI 581 in IMS, see: The IMS Handbook.
- Minimal wall thickness (Tmin) calculators in IMS PEI
Determining the minimum required thickness (Tmin) is critical for maintaining structural integrity under design pressure. IMS PEI supports ASME VIII and ASME B31.3 compliant calculators for vessels, heat exchangers, and piping components, including cylindrical shells, heads, elbows, and nozzle necks. The calculated Tmin value of an equipment defines the minimum required wall thickness that can safely withstand design pressure and mechanical loads without risk of failure. It is often interchangeably referred to as renewal thickness in our IMS. It is essential to note that the renewal thickness does not include the corrosion allowance. By accurately and automatically determining Tmin and allowing IMS PEI to populate it in your corrosion monitoring location (CMLs), our users can ensure that the equipment always operates within the design limits established by standards and codes.
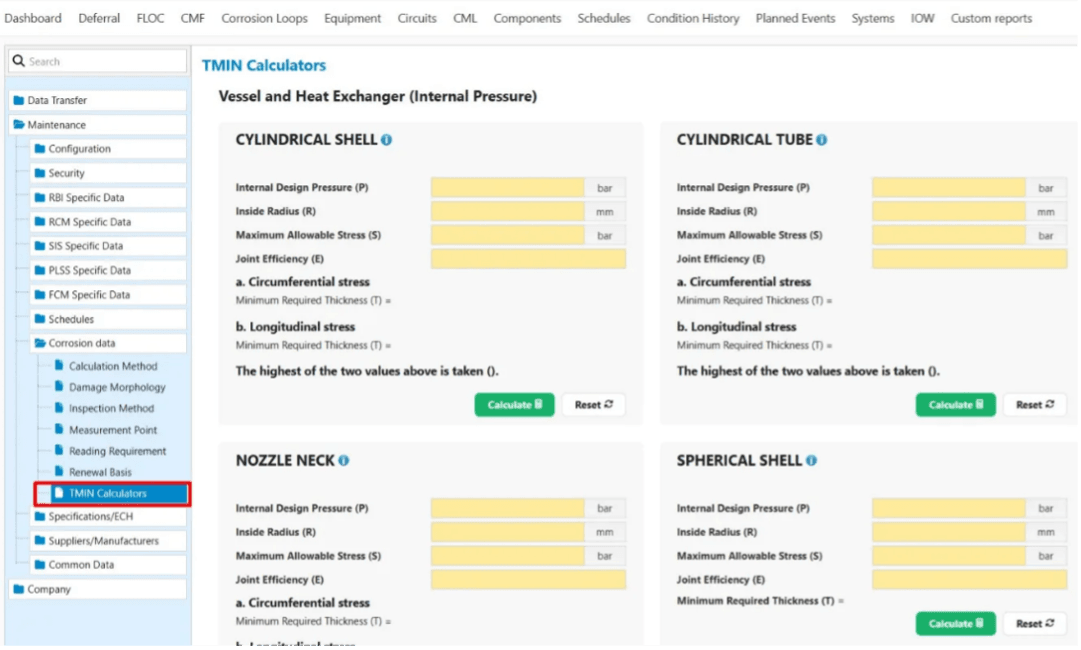
Minimal wall thickness Tmin Calculators in IMS PEI
For more information on TMIN Calculators, see: The IMS Handbook.
- Damage morphology tracking on the CML level in IMS PEI
Inspection workflow for recording measurement set now has the option capture visible damage patterns like cracks or pitting at the CML level in addition to the wall thickness. This morphology data on the CML level enables you to track degradation evolution over time, and filter by morphology for more in-depth insights into asset health.

Display the damage morphologies in the Measurement Set
For more information on capturing damage morphologies, see: The IMS Handbook.
3. Connected ecosystem: Seamless integration of asset integrity data
It is a given that asset integrity data originating from multiple sources must connect cohesively to maintain consistency and compliance across interconnected processes. The real challenge lies in achieving seamless interoperability between systems without compromising data integrity or traceability. Likewise, the integration of your data within IMS is equally crucial to ensure that redundant processes are eliminated. To further improve our existing integration logic within and across IMS, read further on some of our newer enhancements on that front:
- PI data integration and API enhancements for 3rd party system integration across IMS products
Better and faster data synchronization capabilities with PI provide you with more confidence in the data quality. Likewise, our teams have enhanced the API for data handling between IMS and SAP, Maximo, data lakes, and analytics tools.
For more information on interfacing IMS with third-party systems, see The IMS Handbook.
- Enhanced SIS lifecycle management (Deletion & Retirement)
IMS SIS introduces a structured, role-based framework for managing the deletion and retirement of critical safety and integrity objects, including HAZOPs, LOPAs, SIF Analyses, and Equipment Actors. This now ensures that historical records, their dependencies, and associated metadata remain fully auditable, preserving data integrity and compliance throughout the SIS lifecycle.

Batch retirement of multiple HAZOPs, LOPAs and SIF analyses
For more information on deletion and retirement, see: The IMS Handbook.
- Improved syncing of FMEA data between Equipment and SIF Analyses in IMS SIS
We have improved the syncing of FMEA data between Equipment and SIF Analyses, ensuring design integrity and traceability. When a SIF Analysis achieves final approval, IMS automatically updates the related Equipment FMEA records, resets the linked SIF analyses to a draft status, and propagates changes across associated objects.

FMEA data is auto-populated in the SIF analysis
For more information on reviewing and updating FMEA data, see: The IMS Handbook.
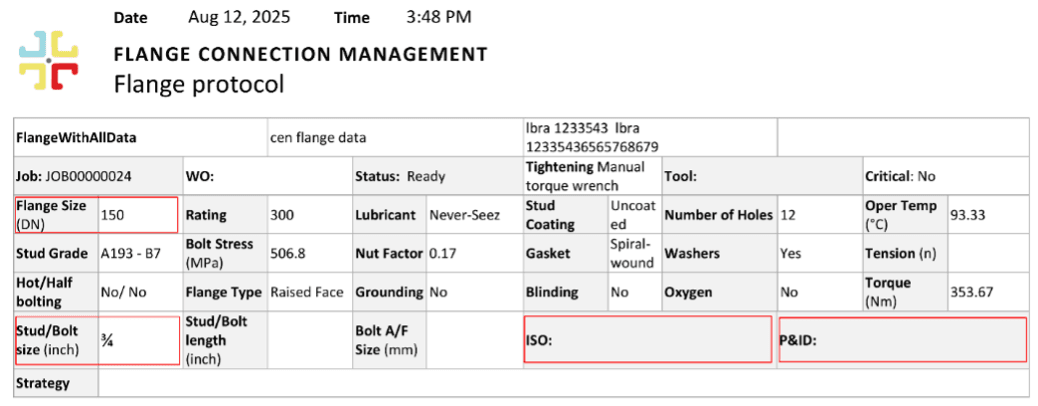
- NEW updated flange protocol report template in IMS FCM
Our Flange Protocol Details Report now features improved readability, unit flexibility, and key fields such as P&ID and ISO numbers—making documentation more precise and complete. This relevant data is pulled in from the flange details page, providing a more complete report and enhancing usability for maintenance and inspection planning.
Ready to explore? Check out these and our other enhancements from this year in our Release Notes and learn what these new improvements can do for you.
Take your IMS knowledge to the next level
Master any IMS module with Cenosco Academy’s self-paced e-learning. Fill out the form below to get started.
Summary and FAQs:
What are the key improvements in the IMS 2025 Q3 and Q4 releases?
The 2025 Q3 and Q4 releases focus on simplifying workflows to boost productivity, enabling informed engineering decisions, and creating a connected ecosystem where asset data flows seamlessly across IMS modules and other systems.
What are Min/Max filters, and how do they work across IMS modules?
Min/Max filters allow you to quickly filter data like earliest inspection dates, most recent condition histories, or lowest remaining life values grouped by relevant properties, eliminating the need for manual sorting or spreadsheet exports.
Does IMS now support API 581 Risk-Based Inspection methodology?
Yes, IMS PEI now supports API 581 RBI methodology (2016 edition, including 2019 and 2020 addenda) in addition to the existing S-RBI approach, with calculations independently validated and certified by SGS for API RP 581 compliance.
What enhancements have been made to IMS drawings and documents management?
Recent improvements include interactive previews without leaving the main grid, one-step equipment linking during upload, custom naming to avoid filename confusion, version replacement capabilities, and enhanced event history with exportable logs.
Are inspection locations now available in all IMS modules?
Yes, inspection locations can now be defined across all modules, extending beyond IMS PLSS to IMS PEI and IMS RCM, making it easier to track where inspections occur and helping field personnel identify activities.
What are the new minimal wall thickness (Tmin) calculators in IMS PEI?
IMS PEI now supports ASME VIII and ASME B31.3 compliant calculators for determining minimum required thickness for vessels, heat exchangers, and piping components, automatically populating Tmin values in corrosion monitoring locations.
How has damage morphology tracking been improved in IMS PEI?
The inspection workflow now allows capturing visible damage patterns like cracks or pitting at the CML level in addition to wall thickness, enabling you to track degradation evolution over time and filter by morphology for deeper asset health insights.
What improvements have been made to third-party system integrations?
Enhanced PI data integration provides better data synchronization confidence, while improved APIs facilitate data handling between IMS and SAP, Maximo, data lakes, and analytics tools.