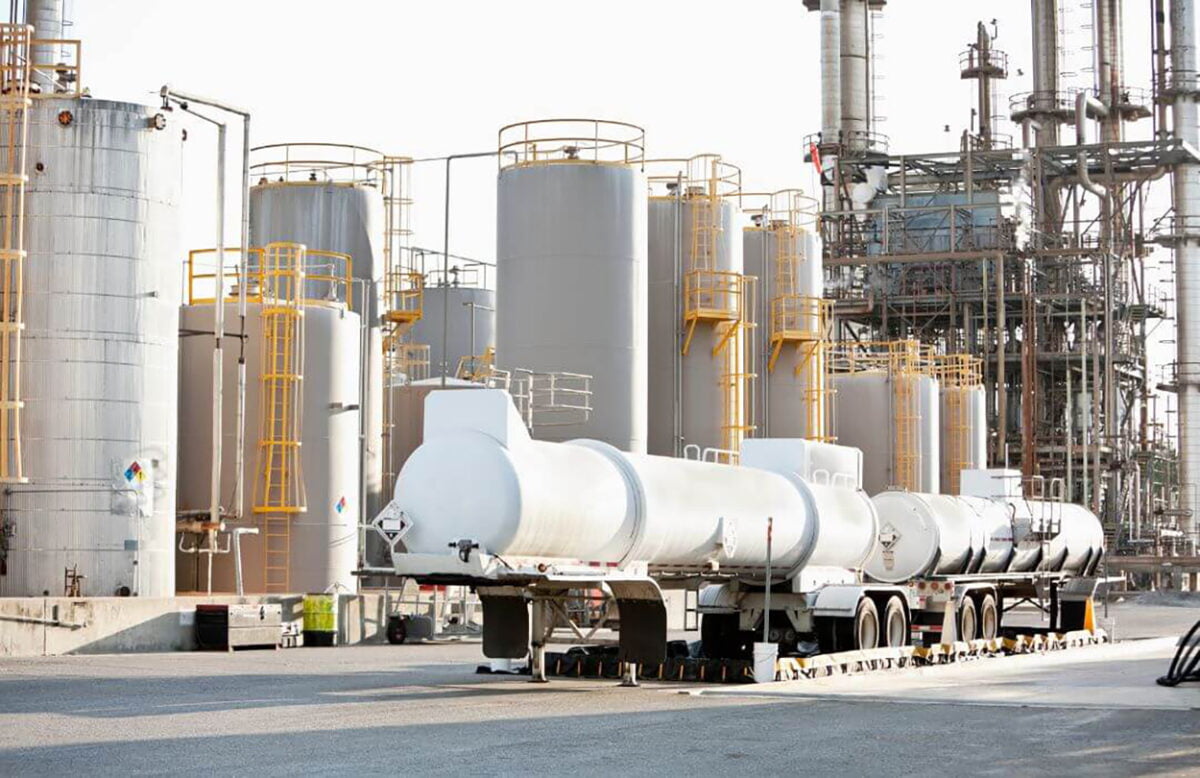
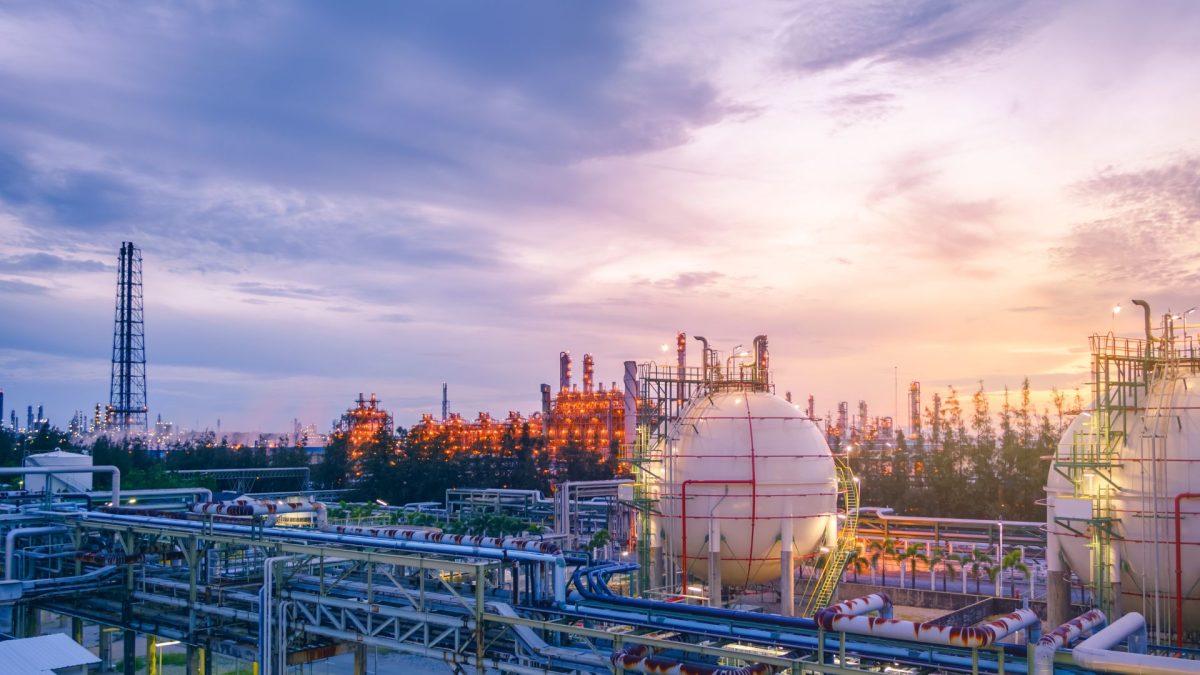
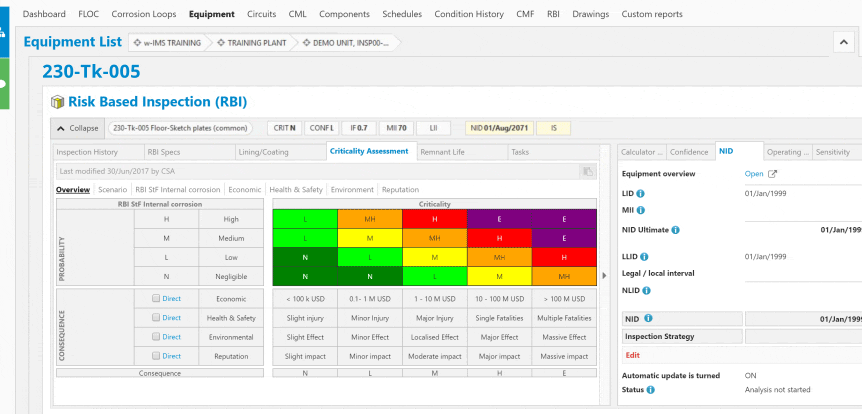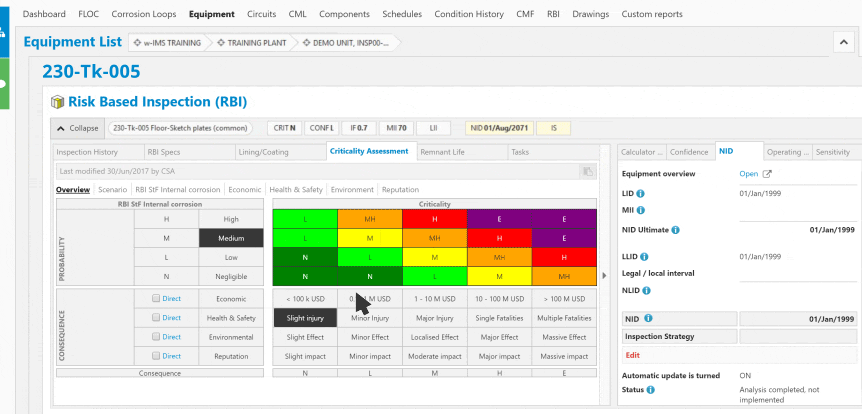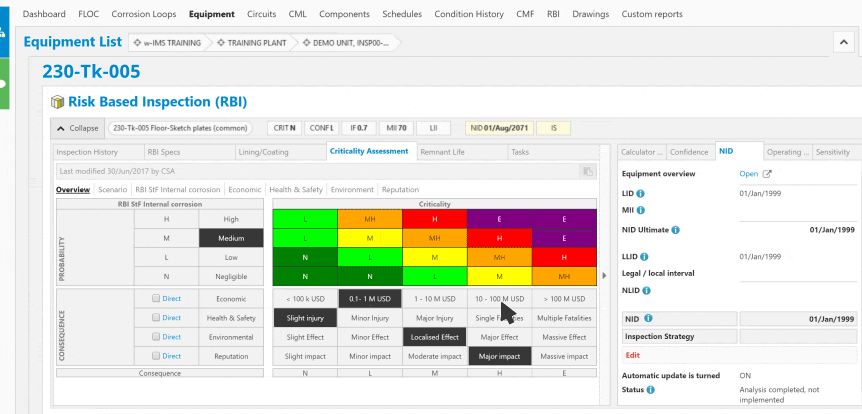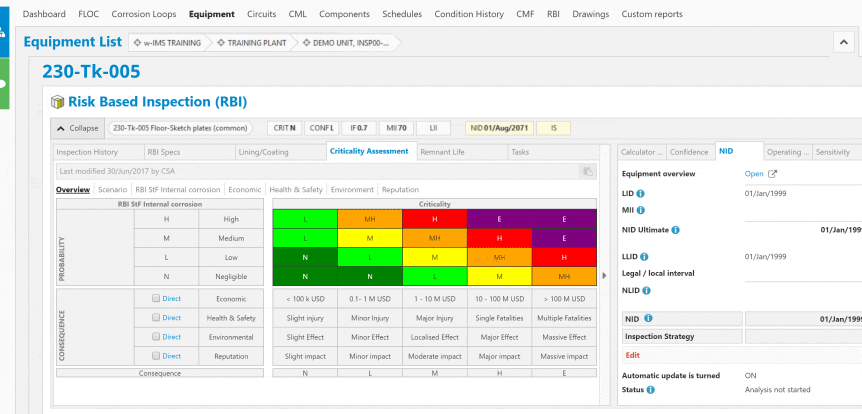
Corrosion control in the oil and gas industry is a critical aspect of maintaining the integrity and safety of infrastructure, equipment, and facilities involved in the exploration, production, refining, and transportation of oil and gas.
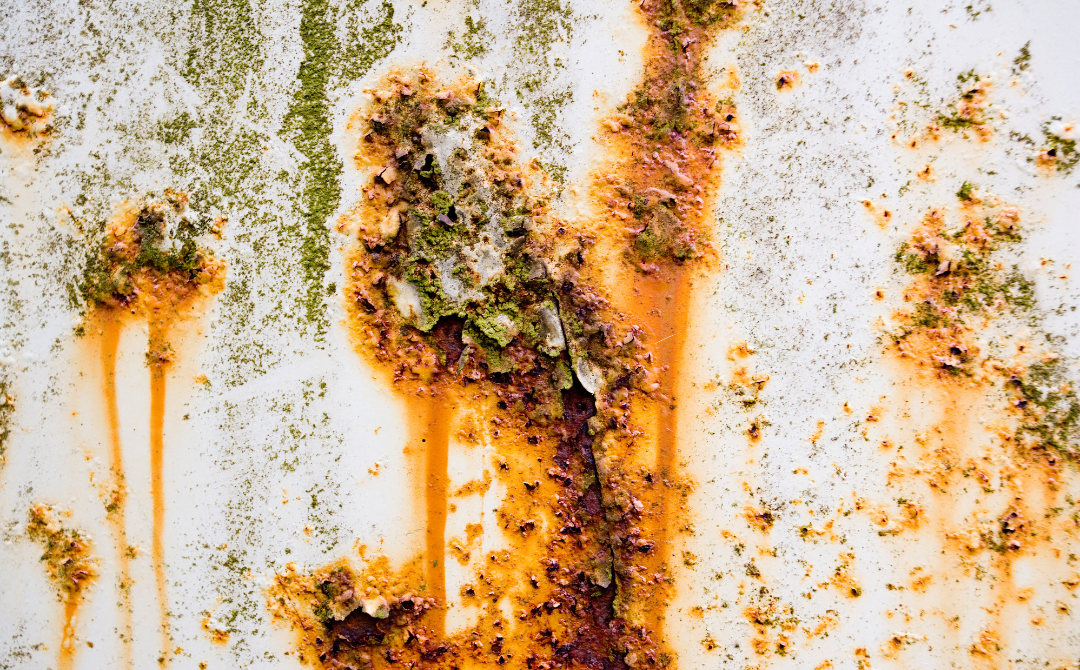
Corrosion refers to the gradual degradation of materials due to chemical reactions with the environment, leading to loss of material, reduced structural strength, and potentially catastrophic failures.
Given the harsh operating conditions and corrosive substances in the oil and gas industry, effective corrosion control is essential to ensure reliable and safe operations.

The Cost of Corrosion in the Oil and Gas Industry
Corrosion-related costs are substantial in the oil and gas industry.
Corrosion-related issues can lead to unplanned shutdowns and reduced productivity.
The global costs of corrosion was estimated to be $2.5 trillion annually, according to estimates from NACE International (formerly known as the National Association of Corrosion Engineers).
A Brief History of Corrosion Control in the Oil and Gas Industry
The history of corrosion control in the oil and gas industry is marked by a gradual understanding of the detrimental effects of corrosion on infrastructure and equipment, as well as the development of increasingly sophisticated techniques to prevent and mitigate its impact.
Here’s a brief overview of the key milestones and developments in corrosion control in the oil and gas industry.
Early Years
- The oil and gas industry emerged in the mid-19th century, and the initial focus was on exploration, drilling, and production.
- As the industry grew, it became apparent that equipment and infrastructure were susceptible to corrosion in the harsh environments where oil and gas were extracted and transported.
Early-20th Century
- In the early 20th century, basic corrosion control methods like coatings and paints were employed to protect equipment and pipelines from corrosion.
- The use of cathodic protection, an electrochemical technique to prevent corrosion, began to gain traction in the 1920s and 1930s. Sacrificial anodes made from less noble metals were introduced to protect more valuable equipment.
Mid-20th Century
- The oil and gas industry experienced significant expansion during and after World War II, which required more advanced corrosion control methods.
- Developing corrosion-resistant alloys (CRAs) and stainless steels offered improved resistance to the corrosive effects of oil, gas, and associated chemicals.
- Research efforts and collaboration among industry professionals led to the establishment of corrosion-related organizations, such as NACE International (founded in 1943), which was key in advancing corrosion science and control techniques.
Late-20th Century
- The 1970s saw advancements in inspection and monitoring techniques, including non-destructive testing (NDT) methods like ultrasonic testing and radiography.
- The oil crises of the 1970s and growing environmental awareness prompted increased emphasis on maintaining the integrity of infrastructure to prevent leaks, spills, and other environmental incidents due to corrosion-related failures.
21st Century
- The 21st century has witnessed further innovations in corrosion control, including the development of “smart pig” inspection tools for pipelines, utilizing advanced sensors and technologies.
- Research into more effective corrosion inhibitors and environmentally friendly coatings has led to improved protection of oil and gas infrastructure.
- Advances in cathodic protection technology, including impressed current systems, have enhanced the ability to safeguard pipelines and other assets.
- The industry continues to invest in research and development to enhance corrosion monitoring, prediction, and mitigation techniques, incorporating data analytics and predictive modeling.
Overall, the history of corrosion control in the oil and gas industry reflects a progression from basic protective measures to sophisticated and technologically advanced methods.
As the industry continues to evolve, the focus on corrosion control remains critical for ensuring safety, environmental protection, and the efficient operation of oil and gas facilities.
Request a Demo
See IMS in action
Why is corrosion control so important in the oil and gas industry?
Corrosion control is vital in the oil and gas industry because the materials and equipment used in extraction, processing, transportation, and storage are exposed to aggressive environments containing corrosive substances such as water, gases, acids, and salts. Corrosion can lead to equipment failure, leaks, and environmental incidents, posing serious safety risks, disrupting operations, and resulting in significant financial losses. Effective corrosion control ensures the integrity, reliability, and longevity of infrastructure, enhances safety, and minimizes the environmental impact of the industry.
What are some common corrosion control methods used in the oil and gas industry?
Several corrosion control methods are employed in the oil and gas industry:
- Coatings and Paints: Protective coatings are applied to surfaces to create a barrier between the material and the environment.
- Cathodic Protection: This technique involves making the structure cathodic in an electrochemical cell to prevent corrosion. It can be achieved using sacrificial anodes or impressed current systems.
- Corrosion Inhibitors: Chemicals are added to fluids to reduce the rate of corrosion by forming a protective layer or altering the environment’s chemistry.
- Material Selection: Using corrosion-resistant alloys, stainless steels, and non-metallic materials in equipment and infrastructure design.
- Regular Inspection and Maintenance: Monitoring and assessing corrosion regularly, followed by maintenance actions such as cleaning, re-coating, or replacing corroded components.
How does the oil and gas industry ensure compliance with corrosion control regulations and standards?
The oil and gas industry is subject to various regulations and standards that govern corrosion control practices. Regulatory agencies, such as the U.S. Pipeline and Hazardous Materials Safety Administration (PHMSA), establish guidelines and requirements for corrosion control in pipelines and other facilities. Compliance involves implementing appropriate corrosion control measures, conducting regular inspections, and adhering to reporting and documentation requirements. Additionally, industry organizations like NACE International provide guidelines, standards, and best practices for corrosion control that companies often adopt to ensure safe and environmentally responsible operations.
Using advanced Asset Integrity Management Software for your Corrosion Control, you can ensure to meet compliance and regulations in your area. Read more about the leading industry software, or request a demo to get started.