The Safety Integrity Levels (SIL) are a measure of the safety performance of a system. Starting from SIL 1, each level higher provides additional requirements of safety measures. In this blog, we will focus on the main differences between SIL 1, 2, 3, and 4 and their characteristics.
SIL 1, 2, 3, and 4: What is the difference?
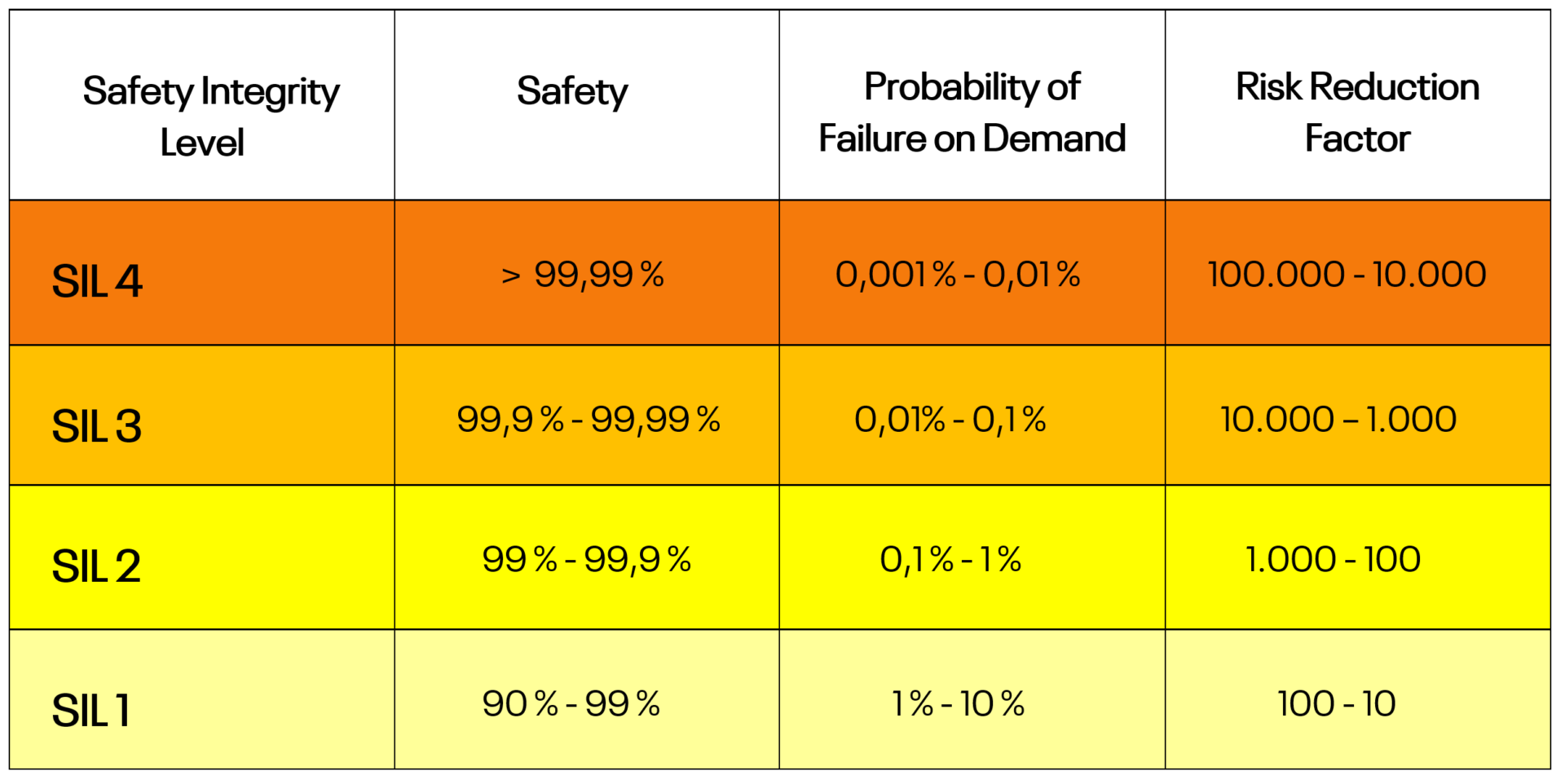
While SIL 1 typically offers basic safety measures, SIL 2 requires stricter measures, followed by SIL 3, which requires higher safety standards. SIL 4, which is the peak of safety integrity, exceeds even SIL 3 in its strictest requirements. SILs define the degree of risk reduction provided or required by an instrumented safety function (SIF). SILs are defined based on the range of the Risk Reduction Factor, with SIL 1 starting with an RRF between 10 – 100 and SIL 4 with an RRF between 10000 – 100000.
Different SIL across industries
The application of SIL depends on the level of safety performance required in different industrial situations:
What is SIL 1?
SIL 1 is often used for systems that require just minimum safety measures. It’s suitable for applications with low risk and failure consequences that are not severe. SIL 1 systems use predefined safety functions that are properly implemented and verified on a regular basis to ensure safety. This covers businesses such as manufacturing, food processing, and building automation, where failures are less harmful.
What is SIL 2?
SIL 2 is used for systems that demand higher levels of safety performance than SIL 1.
It’s used for applications with intermediate risk and for more severe failure consequences than SIL 1 systems. SIL 2 systems contain more strict safety measures to minimize risk failures and ensure safety in various industry areas. SIL 2 is widely used in industries with moderate risk levels and where failures could have serious effects. Chemical processing, pharmaceuticals, and power generation companies frequently use SIL 2 to improve safety precautions.
What is SIL 3?
SIL 3 ratings are utilized in systems with high-risk failures. Moreover, it provides very strict safety measures, reducing the risk of catastrophic failures significantly. Industries that face high-risk scenarios with potentially catastrophic effects frequently choose SIL 3. Industries such as oil and gas, petrochemicals, and nuclear power rely on SIL 3 to provide the greatest level of safety and reliability in key systems and processes.
What is SIL 4?
SIL 4 is the highest possible standard of safety performance. It’s used in systems where failure could have catastrophic consequences, including fatalities or irreversible environmental damage. SIL 4 requires the most rigorous safety measures to be taken; it is even stricter than SIL 3. SIL 4 is chosen by industries that operate in extremely dangerous environments, such as aerospace, defense, and some areas of nuclear power generation, in order to guarantee the highest level of safety and reliability in their essential systems and procedures.
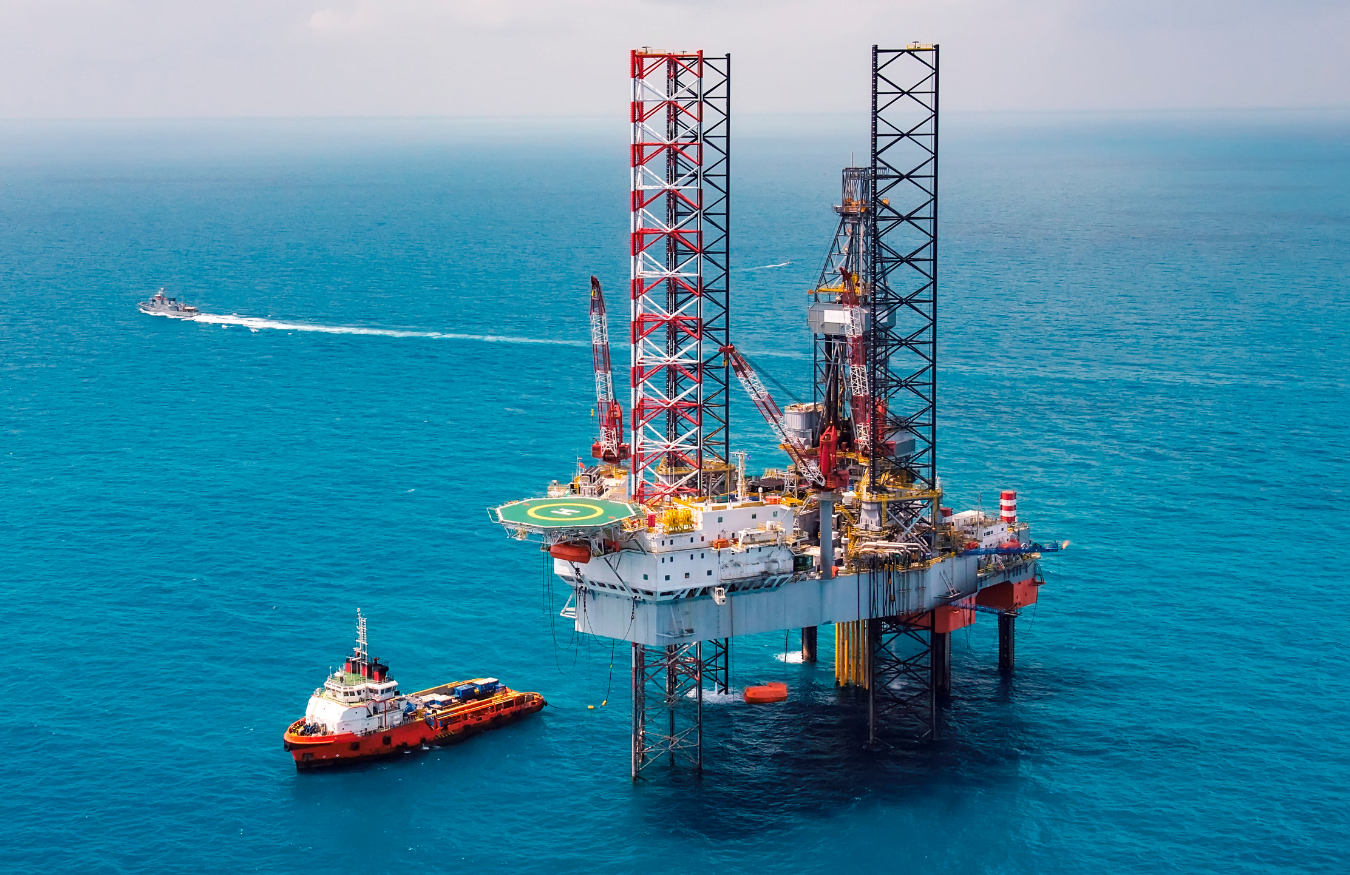
SIL 1, 2, 3, and 4 in the Oil and Gas Industry
In the oil and gas business, SIL is utilized to assure safe operations in extreme conditions, particularly in drilling and production equipment. These levels are part of a risk-based approach to ensuring safety, particularly in the design and implementation of safety instrumented systems (SIS).
Applications of SIL Levels in the Oil and Gas Industry
SIL 1 is applied to safety systems for simple process shutdowns or alarms of minor alterations from normal operating conditions.
SIL 2 is used for emergency shutdowns, fire and gas detection, or overpressure protection. These systems are essential for minimizing risks associated with potential equipment failures.
SIL 3 is crucial for preventing catastrophic events such as fires, explosions, or toxic releases. Safety systems designed to achieve SIL 3 must undergo rigorous analysis, design, and testing to make sure they can effectively minimize the highest level of risks associated with high-pressure or high-temperature processes. It’s standard for drilling and production equipment that ensures safe operations in unfavorable situations, and it is especially crucial for OEMs and operators who cannot afford failures in safety systems.
SIL 4 may be used in extremely high-risk scenarios where failure could lead to catastrophic events with severe consequences, such as large-scale explosions, fires, or environmental disasters. These scenarios might include critical safety systems in offshore drilling platforms, high-pressure and high-temperature processing facilities, or transportation systems for hazardous materials.
While SIL 4 is less commonly applied compared to SIL 3 in the oil and gas sector due to the significant complexity and cost associated with achieving and maintaining SIL 4 levels, it may be considered in specific areas where the consequences of failure are considered unacceptable and where the highest level of safety integrity is required.
Risk Assessment and Certification
SIL is defined as the relative level of risk reduction provided through a safety function and determined through a risk assessment. A risk assessment determines the target SIL for an application or process, which is then required for the final system. The specific safety integrity level (SIL 1, 2, 3, or 4) defines the development requirements that must be completed in order to meet the overall risk reduction goal.
Each component in the functional safety system must be certified to meet the specified SIL. Although product certifying bodies can certify to any standard, they may not be accredited for that standard, resulting in no third-party certification of their ability.
In the oil and gas business, functioning safety system components such as flame and gas detectors must be certified to meet particular criteria, including a facility’s goal Safety Integrity Level (SIL). The certifying bodies tasked with determining SIL compliance may not be accredited to conduct every certification they take on, resulting in a lack of official validation of proficiency and potential safety risks.
Calculating SIL levels with IMS SIS
Specialist software can greatly simplify SIL calculations, studies, and compliance. IMS SIS is a top choice in the industry, offering powerful tools for HAZOP studies, LOPA studies, and SIF analyses—where SIL levels are calculated and Safety Instrumented Functions (SIFs) are designed. It helps companies efficiently manage SIL requirements, perform risk analysis, and design systems, ensuring maximum safety and reliability.
IMS SIS is guided by international standards such as IEC 61508 and IEC 61511, which not only shapes the design but also the maintenance of SIFs according to their assigned SIL. This maintenance includes regular testing, which IMS SIS also supports by facilitating the planning, execution, and documentation of SIF tests.
IMS SIS can help industries operate confidently and efficiently while safeguarding people, assets, and the environment.
A single software tool for all your functional safety management
IMS SIS features bidirectional data synchronization between modules, ensuring up-to-date safety function data and consistent achievement of the required SIL. Designed to meet and exceed the highest industry standards for Safety Integrity Levels (SIL), each system undergoes rigorous testing and validation to ensure reliable performance under demanding conditions. With advanced technologies and comprehensive safety measures, IMS SIS minimizes risks and enhances operational efficiency, making it an ideal choice for industries requiring stringent safety protocols.





